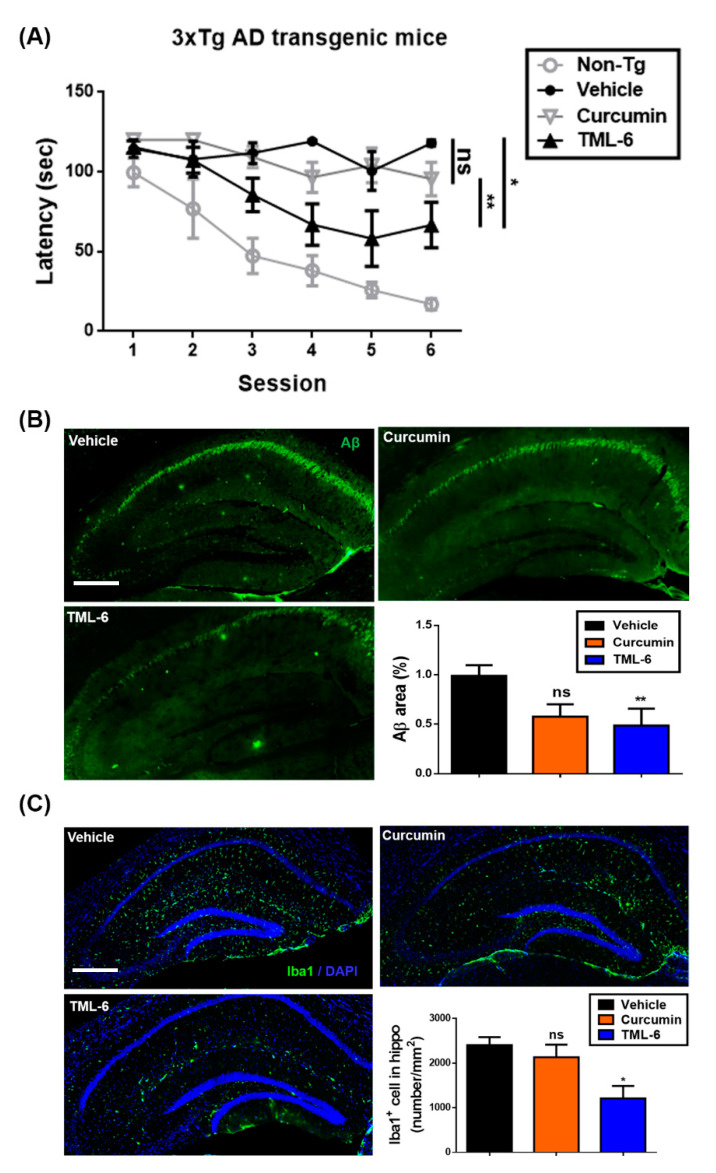
Figure 4.
TML-6 improved the behavior test and reduced the brain levels of Aβ and the inflammatory biomarker Iba1 in the 3x-Tg AD mouse model. (A) Six-month old 3x-Tg AD mice were fed with normal diets (vehicle), or diets containing traditional curcumin and TML-6 for four months at a dosage of 150 mg/kg (each group contained five mice, n = 5). After four months of treatment on the experimental diet, animals were subjected to a behavior test in the form of the Morris water maze. The figure shows data from vehicle, curcumin and TML-6 fed different chow diets, with triplex-Tg AD mice and non-transgenic mice (Non-Tg) serving as the control. (B) The Aβ levels in mouse brains in 3x-Tg AD mice were examined at the end of behavior test after four-month feeding with the treatment of normal diets, traditional curcumin and TML-6. Mouse brain sections were examined by immunofluorescence staining. The immunofluorescence staining of Aβ was quantified and is represented in the panel. Scale bar: 200 μm. (C) Mouse brain sections were also examined for the inflammatory biomarker Iba1 by immunofluorescence staining. The images of Iba-1 levels were represented and quantified as indicated in the panel. The significance of the behavior test, Aβ, and Iba-1 levels between the mice treated with normal diets (vehicle) and either curcumin or TML-6 was determined by paired t-test. Asterisks denote data representing the mean with a standard deviation (SD) error bar, and p value < 0.05 was considered significant (* p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01).