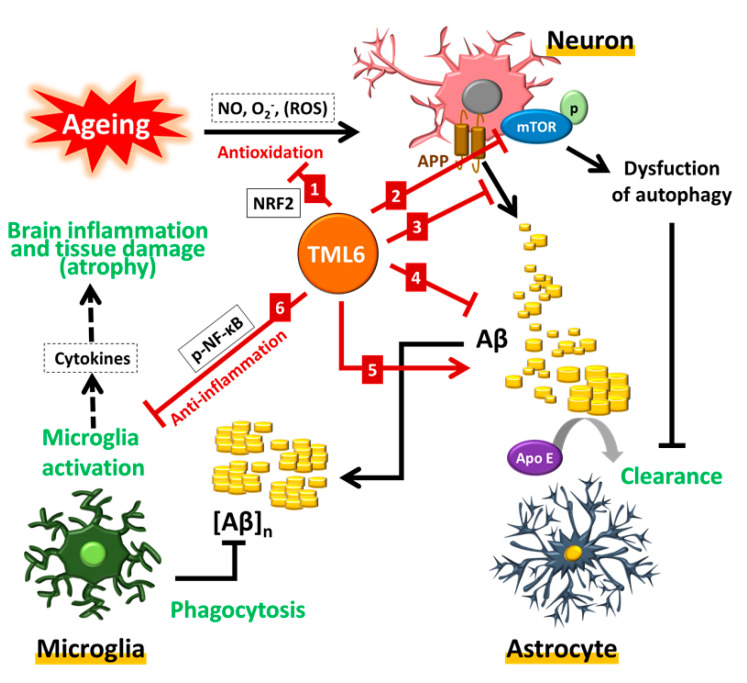
Figure 6.
A hypothetical scheme on the potential action mechanism of TML-6 in the therapy of Alzheimer’s disease. Curcumin derivative-TML-6 treatments can induce (1) transcriptional activation of the Nrf2 promoter, which can reduce free radicals, the hallmark of the aging process; (2) following the aging process, the dysfunction of autophagy machinery and activation of mTOR will reduce the autophagolysosomal function to remove the misfolded proteins and lead to the accumulation of Aβ. TML-6 can effectively inhibit the phosphorylation of mTOR and maintain the normal function of autophagy to assure Aβ clearance; (3) TML6 can inhibit the production of Aβ from APP and (4) suppress the synthesis and secretion of Aβ from neurons; (5) TML6 can transcriptionally activate APOE and enhance the clearance of Aβ; (6) TML6 can inhibit the activation of microglial cells and reduce inflammatory injuries in the brain. The future design of therapeutics should combine targeting APP/the Aβ cascade and improving aging-related biological processes.