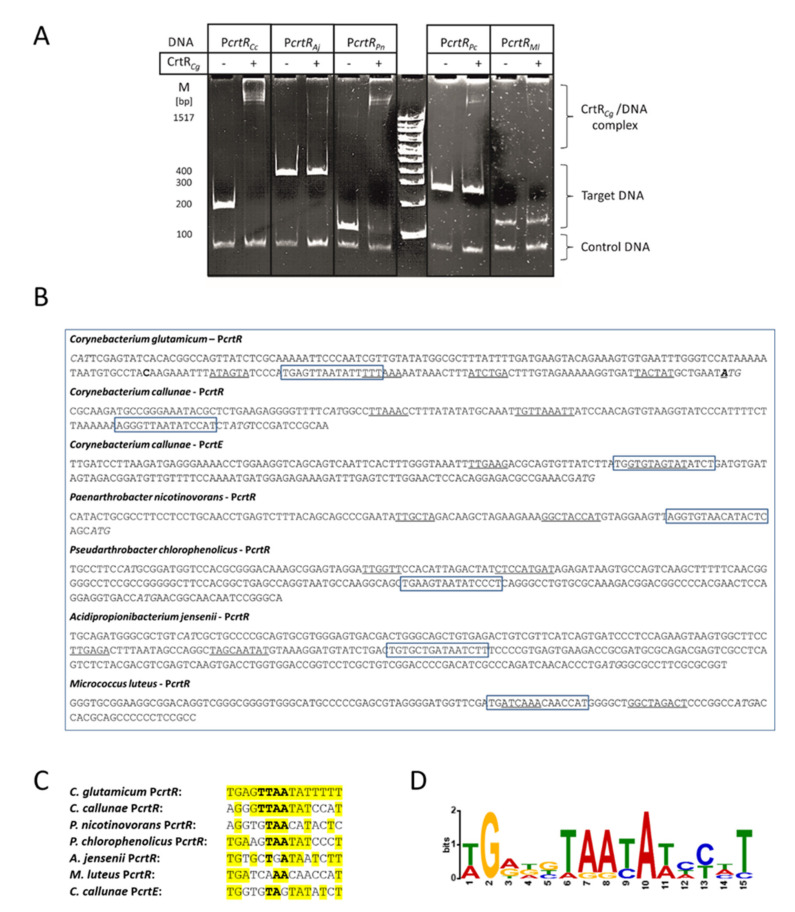
Figure 3.
Characterization of CrtR from C. glutamicum in vitro. (A) Bandshift assays of His-tagged CrtR protein from C. glutamicum (CrtRCg) and the intergenic DNA sequences between the crtR orthologs from C. callunae, A. jensenii, P. nicotinovorans, M. luteus and P. chlorophenolicus, and the respective divergently transcribed genes. (B) Putative -10 and -35 promoter DNA sequences (underlined), translation start codons (italics) and the putative conserved CrtR binding sequences (boxed). The mapped transcriptional start sites of C. glutamicum crtR and crtE are given in bold. (C) Putative conserved CrtR binding sequences (conserved nucleotides are given in yellow; the TTAA sequence that was shown previously to be required for C. glutamicum CrtR binding by mutational analysis is depicted in bold face). (D) The graphical representation of the derived consensus DNA binding motif of the CrtR proteins from C. glutamicum, C. callunae, A. jensenii, P. nicotinovorans, M. luteus and P. chlorophenolicus (designed using WebLogo).