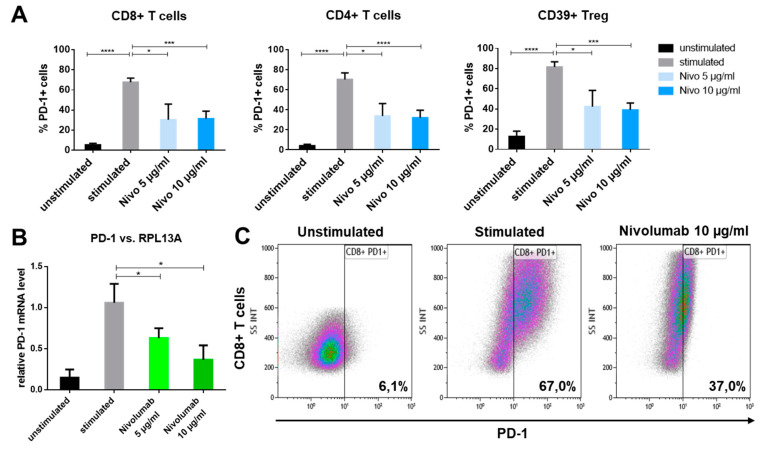
Figure 6.
Different concentrations of nivolumab were applied in vitro to lymphocytes for 3 days. (A) Subsequent fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis revealed a reduction of PD-1 expression after nivolumab (nivo) treatment on all analyzed T cell subsets (n = 5 healthy donors). (B) A similar significant reduction was shown on PD-1 mRNA by RT-PCR of nivolumab-treated lymphocytes. RPL13A was used for normalization of mRNA levels (n = 3 healthy donors). (C) Representative density plots of CD8+ T cells showing the reducing effect of in vitro nivolumab treatment on PD-1 expression. p-values < 0.05 were considered to be significant with (*), p-values < 0.001 (***) and p-values < 0.0001 (****).