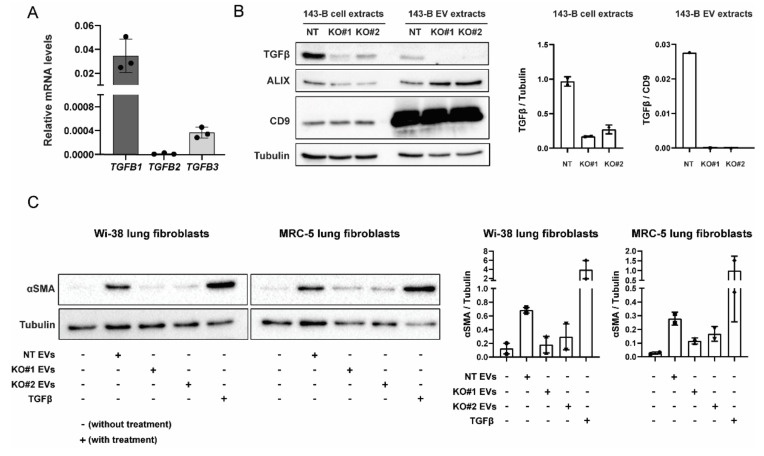
Figure 5.
CRISPR-Cas9-mediated knockout of TGFB1 prevents 143-B-derived EVs from inducing lung fibroblast differentiation. (A) mRNA expression levels of indicated TGFβ isoforms (relative to GAPDH) in 143-B osteosarcoma cells as determined by qRT-PCR. (B) Western blot analysis of TGFβ1 protein expression was used to validate the efficiency of CRISPR-Cas9-mediated genome editing in non-targeting control (NT) 143-B, TGFβ1 KO#1 143-B, and TGFβ1 KO#2 143-B cell extracts and, respectively, derived-EV protein extracts. Cell extracts were harvested 4-5 passages after the initial viral transduction. Protein levels of EV markers (CD9 and ALIX) were examined by Western blot. (C) Western blot analysis of αSMA expression in WI-38 fibroblasts and MRC-5 fibroblasts following 48 h incubation with 20 μg/mL of EVs derived from control NT 143-B cells, TGFβ1 KO#1 143-B cells and TGFβ1 KO#2 143-B cells. Soluble TGFβ (10 ng/mL was used as the positive control. Tubulin was use as a loading control. Representative Western blots (left panels) and respective quantitative analysis of two independent experiments (right panels).