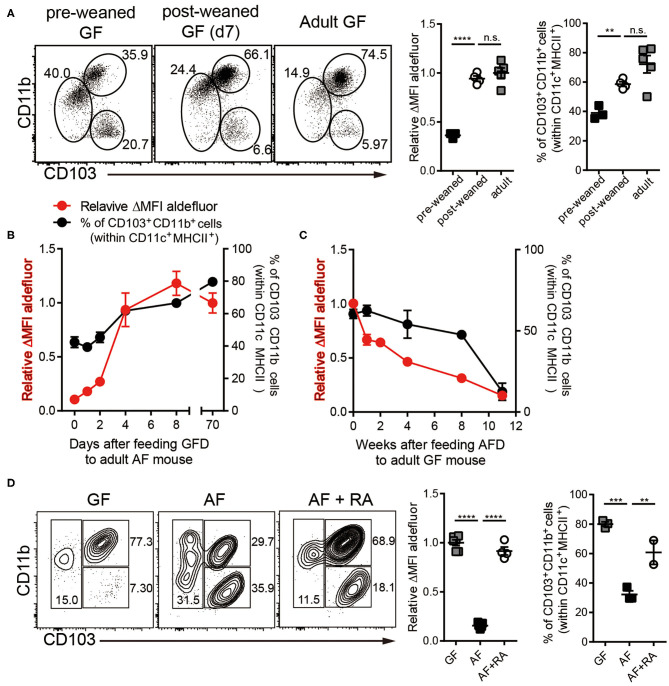
Figure 2.
Dietary components in normal chow readily trigger and maintain RALDH activity in siLP-DCs in mice after weaning. Cell suspensions prepared from siLP were subjected to ALDEFLUOR assays and RALDH activity in CD103+CD11b+ siLP-DCs and percentage of siLP-DC subpopulations in CD11c+MHC-II+ cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. (A) GF mice (3-weeks old) before weaning (pre-weaned), GF mice weaned onto NCD for 7 days and adult GF mice were analyzed. (B) RALDH activity and frequencies of siLP-DC subpopulations in CD11c+MHC-II+ cells in adult AF mice (8~12-week-old) after feeding NCD for 0, 1, 2, 4, 8, and 70+ days. (C) RALDH activity and frequencies of siLP-DC subpopulations in CD11c+MHC-II+ cells in adult GF mice (8~12-week-old) after feeding AFD for 0, 1, 2, 4, 8, and 11+ weeks. (D) RALDH activity and frequencies of siLP-DC subpopulations in CD11c+MHC-II+ cells in adult GF, AF, or AF mice that were administered intra peritoneal injection of all-trans RA (500 μg per mouse in soybean oil) every other day for 7 days. Data are combined from two to three independent experiments. MEAN ± SEM are indicated. (B,C) Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA with Turkey's multiple comparison test. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, n.s., not statistically significant.