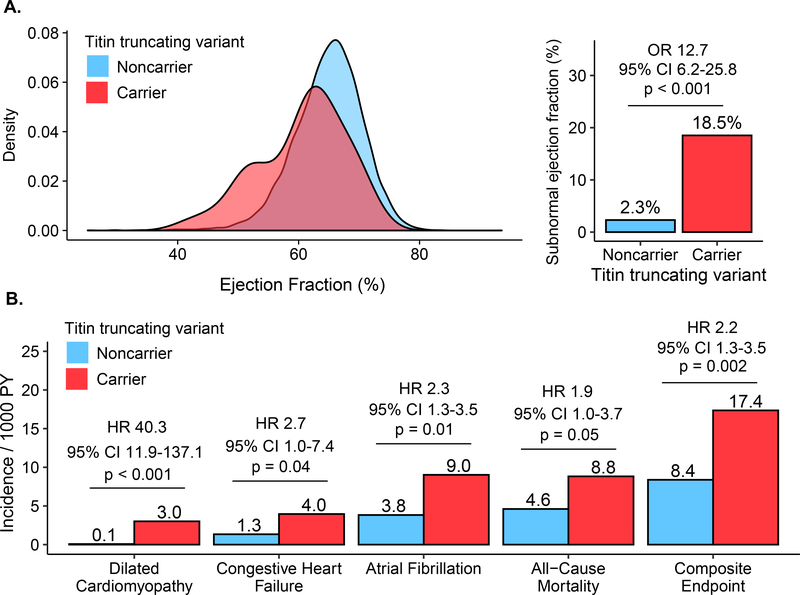
Figure 1: Left ventricular ejection fraction and incident cardiovascular disease in TTNtv carriers versus noncarriers.
(A) Shown is the distribution of left ventricular ejection fraction and prevalence of subnormal ejection fraction among 54 TTNtv carriers and 12,499 noncarriers. In a logistic regression model adjusted for the cubic spline of age, sex, and genetic ancestry, TTNtv carriers had 12.7-fold (95%CI 6.2 – 25.8; p< 0.001) increased risk of a subnormal ejection fraction. (B) Shown are the incidence rates per 1,000 person-years for the composite endpoint and each of its components. Hazard ratios (HR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated using a Cox regression model adjusted for the cubic spline of age, sex, and genetic ancestry.