Figure 8.
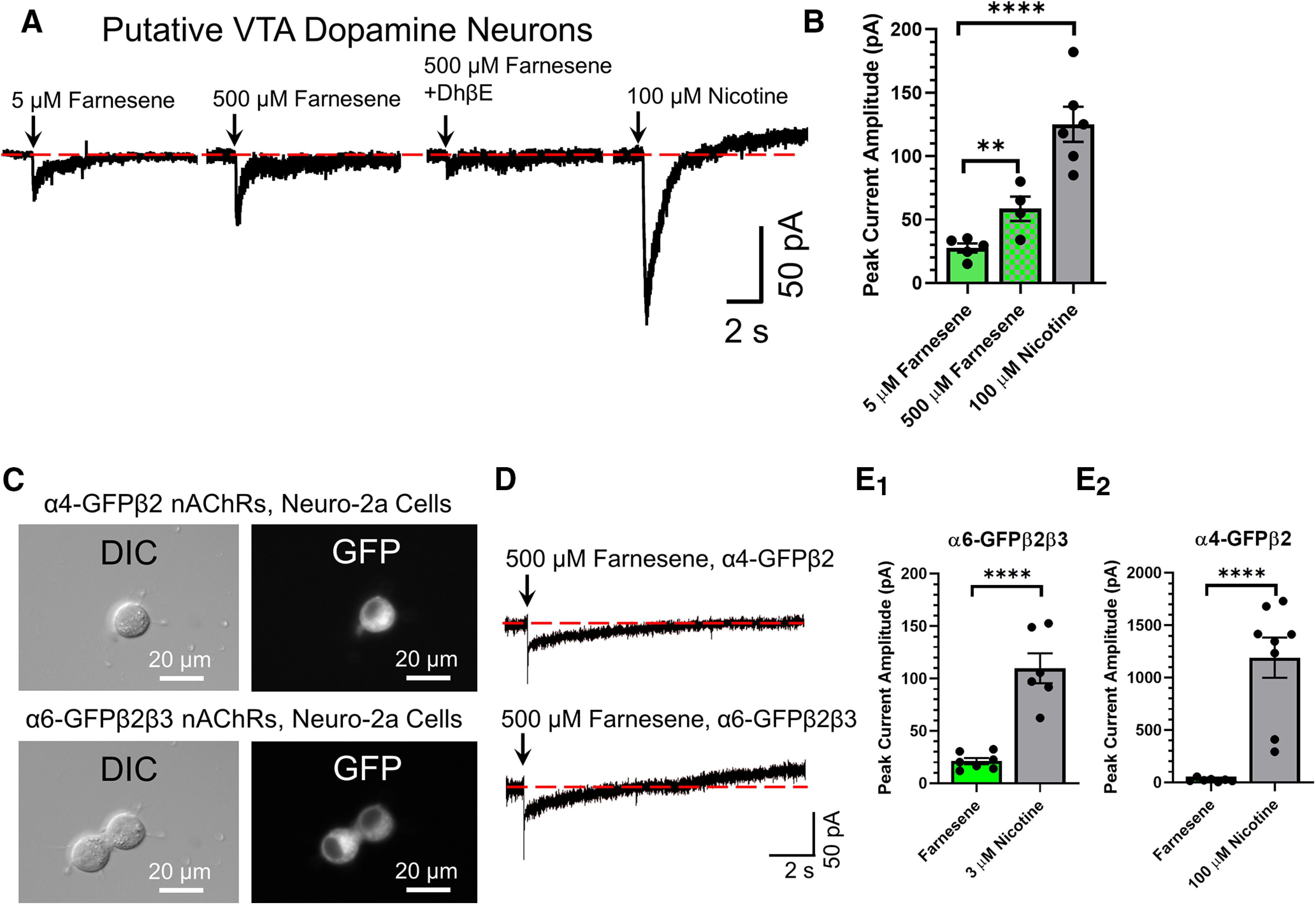
Farnesene acts as a partial agonist on nAChRs. A, B, Voltage-clamp recordings from putative VTA dopamine neurons. A, Five and 500 μm farnesene and 100 μm nicotine were applied to putative VTA dopamine neurons. The β2* nAChR antagonist, DhβE (0.3 μm) blocked inward currents stimulated by 500 μm farnesene. B, Mean peak current amplitude for farnesene and nicotine applications on pDA neurons in the VTA. C–E, Voltage-clamp recordings from neuro-2a cells transiently transfected to contain α4-GFPβ2 and α6-GFPβ2β3 nAChRs. C, Representative images of neuro-2a cells that contain α4-GFPβ2 or α6-GFPβ2β3 nAChRs. D, Representative inward currents stimulated by 300-ms applications of 500 μm farnesene on neuro-2a cells containing α4-GFPβ2 or α6-GFPβ2β3 nAChRs. E1,2, Mean peak current amplitude of 500 μm farnesene and nicotine applications (3 and 100 μm nicotine for α6-GFPβ2β3 and α4-GFPβ2 nAChRs, respectively) on neuro-2a cells containing nAChRs. B, E1,2, Data are mean ± SEM; **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001; one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey (B) or unpaired t test (E). Dots represent data from individual neurons or cells. Exact p values are given in Results.
