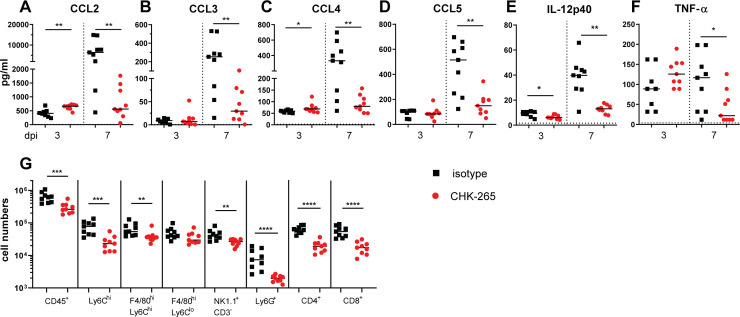
Fig 5. CHK-265 treatment results in reduced pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and immune cell infiltration in musculoskeletal tissue.
Four-week-old WT male and female C57BL/6 mice were administered 100 μg of CHK-265 prior to infection with RRV. (A-F) Ipsilateral quadriceps muscles were harvested 3 or 7 dpi and analyzed for cytokine and chemokine levels. Bars indicate median values (n = 8–9 per group; two experiments; Mann-Whitney test; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). (G) At 7 dpi, ipsilateral quadriceps muscles were digested, single cell suspensions were stained for CD45+ leukocytes, Ly6Chi monocytes, F4/80hiLy6Chi monocyte-derived macrophages, F4/80hiLy6Clo tissue resident macrophages, NK1.1+CD3- NK cells, Ly6G+ neutrophils, CD4+ T cells, or CD8+ T cells, and analyzed by flow cytometry. Bars indicate median values (n = 9 per group; two experiments; Mann-Whitney test; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001).