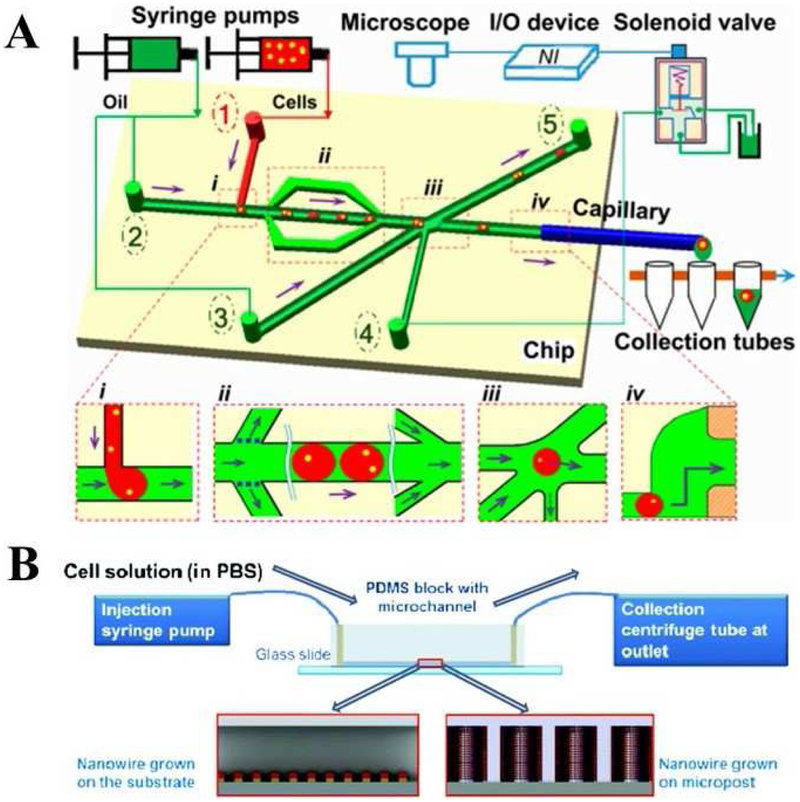
Fig. 3.
Microfluidic single-cell manipulation including cell isolation using droplet microfluidics (A) and cell lysis (B). (a) Schematics of a passive droplet-based microfluidic platform for single cell isolation, including (i) cell encapsulation, (ii) droplet deceleration, (iii) sorting of single-cell droplets, and (iv) export of single-cell droplets into tubes. Adapted with permission from Ref. [86]. Copyright 2017 Springer Nature Publishing. (B) Experimental setup of mechanical cell lysis using a nanowire integrated microfluidic device including: Injection of the cell solution through the microchannel by using the syringe pumps; Anchoring, stretching and bursting of the cells on the nanowire arrays; Centrifugation and collection of a cell solution. Adapted with permission from Ref. [87]. Copyright 2012 The Royal Society of Chemistry.