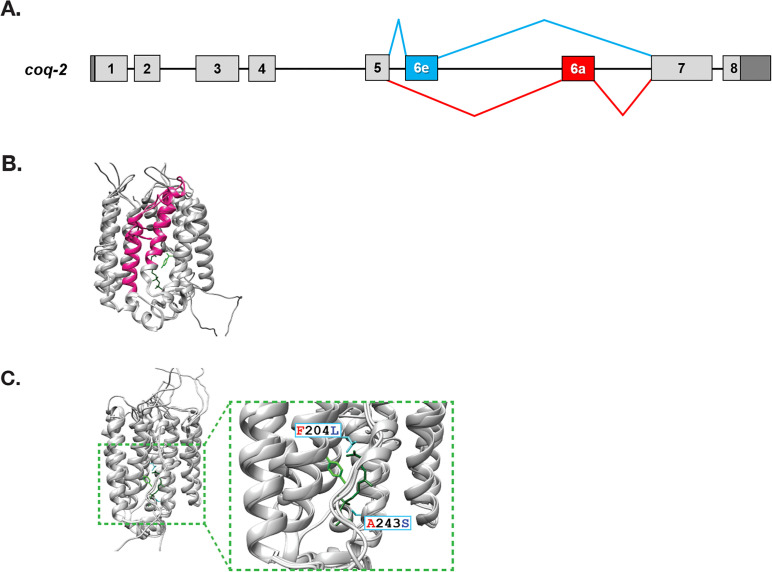
Figure 2. C. elegans coq-2 gene model.
(A) The coq-2 gene contains two mutually exclusive exons, 6e (blue box) and 6a (red box), that are alternatively spliced (blue and red lines, respectively) generating two COQ-2 isoforms. Light gray boxes represent coding sequences of exons 1–5 and 7–8, black lines represent introns, and dark gray boxes denote 5´and 3´ untranslated regions of exons 1 and 8. (B) Alternative splicing of COQ-2 changes the enzyme core. The sequences of C. elegans coq-2a and coq-2e were threaded onto the crystal structure of the apo-form of the Aeropyrum pernix COQ-2 homolog (PDB: 4OD5) in Chimera using Modeller. The region switched by mutually exclusive alternative splicing is shown magenta color. (C) The alternative exons found in all RQ-synthesizing species have two residues that are invariant (L204 and S243 show in cyan; C. elegans numbering) that are near the binding site of the two substrates. Substrates are the polyprenyl tail (dark green; geranyl S-thiolodiphosphate in the crystal structure), and the aromatic ring (light green; p-hydroxybenzoic acid [4HB] in the crystal structure). Note that COQ-2 is rotated from panel B to panel C for clarity.