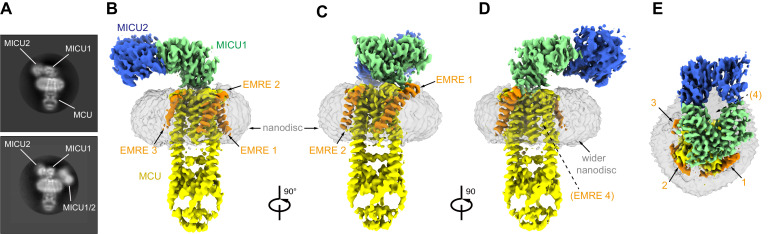
Figure 1. Cryo-EM reconstruction of the holocomplex.
(A) 2D class averages showing side-views of complexes with one or two MICU1-MICU2 heterodimers associated (top and bottom panels, respectively). (B–E) Cryo-EM reconstruction of the holocomplex, shown in orthogonal views. Densities are colored accordingly: MCU (yellow), EMRE (orange), MICU1 (green), MICU2 (blue), and nanodisc (semitransparent gray). Numbers in (E) represent the locations of EMRE subunits. The location of where EMRE 4 would be expected to bind is indicated by parentheses (D–E).
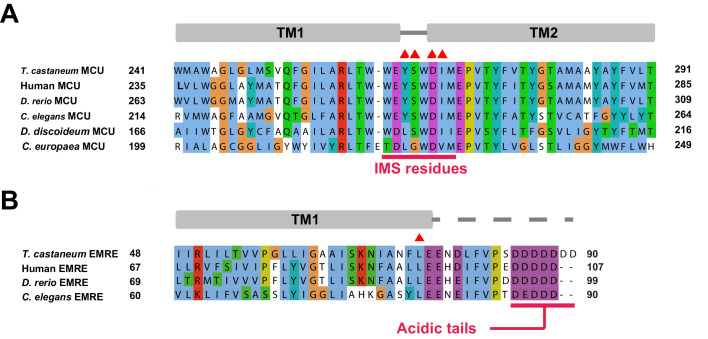
Figure 1—figure supplement 1. Sequence alignments of MCU and EMRE.
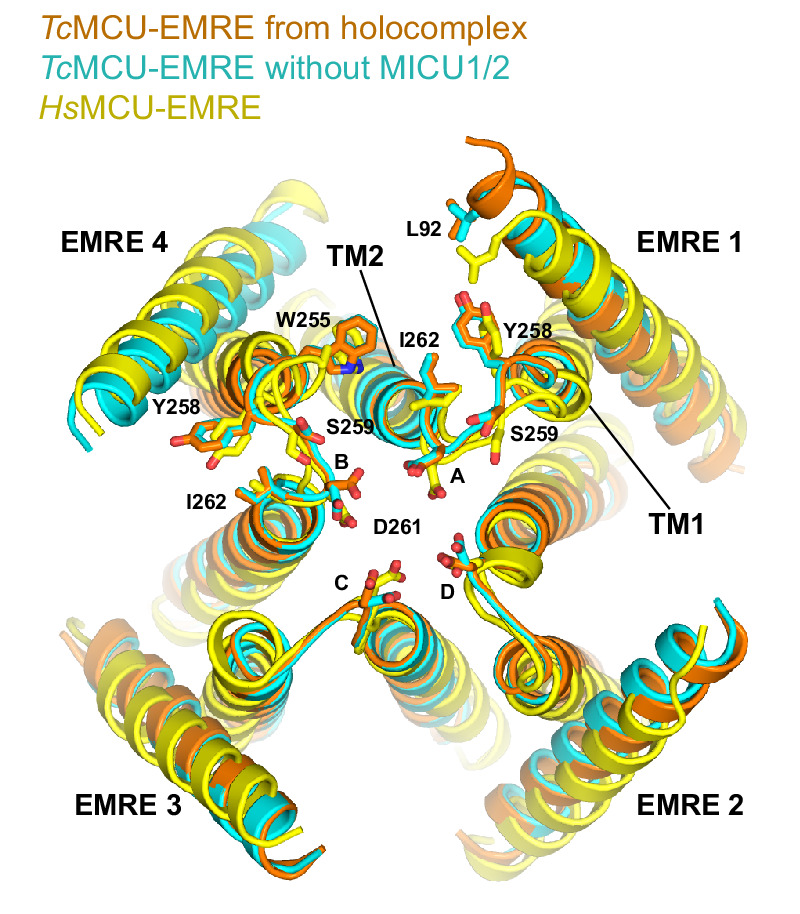
Figure 1—figure supplement 2. Comparison of the MICU1 receptor sites in human and beetle MCU-EMRE complexes.