Fig. 2.
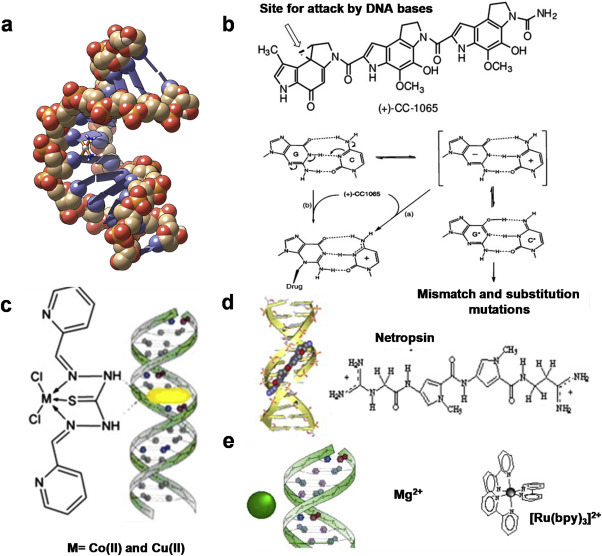
Different modes of drug-DNA interactions (a) Cisplatin is covalently bonded to DNA. Adapted with permission from Ref. [36] (b) Proposed mechanisms for the alkylation of N3 guanine by (+)-CC1065 (c) Intercalation of Co(II) and Cu(II) metal complexes of N1,N5-bis[pyridine-2-methylene]-thiocarbohydrazone (d) DNA complexed with netropsin, a minor groove binder (e) External association of the complex in the atmosphere of ions of the DNA polyelectrolyte. Adapted with permission from Ref. [19].
