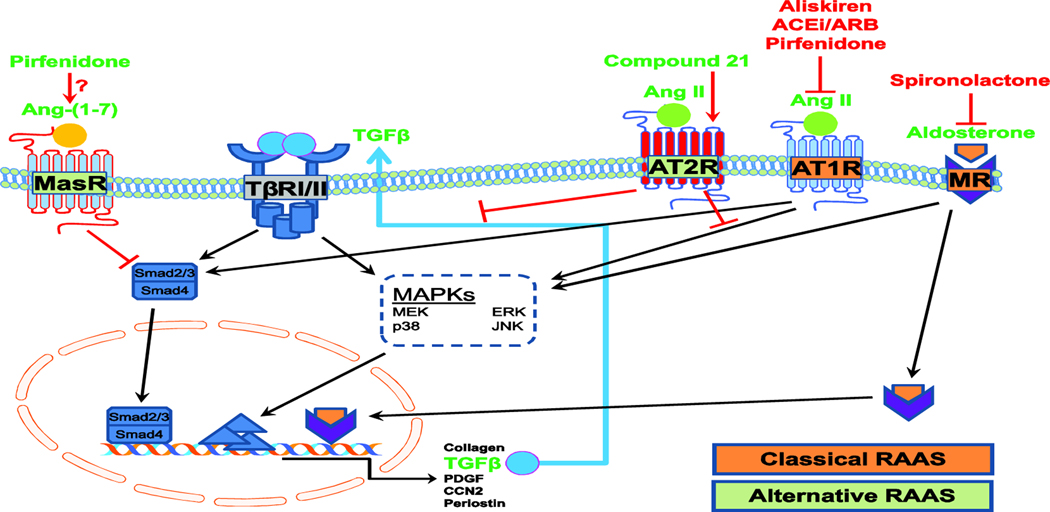
Figure 2. Schematic representation of the interactions of TGFβ and RAAS signaling.
Ligand activation of TGFβ receptors leads to Smad2/Smad3 phosphorylation, leading to recruitment of Smad4 and translocation to the nucleus to activate transcription of fibrotic genes such as collagen, TGFβ, PDGF, CCN2 and periostin. TGFβ also activates non-canonical pathways via MAPKs such as ERK, JNK and p38.Binding of AngII to its type 1 receptor (AT1R) activates MAPKs and Smads, leading to synthesis and release of TGFβ and creating a positive feedback loop to amplify fibrotic TGFβ signaling. Aldosterone activation of mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) induces transcriptional activation of pro-fibrotic proteins. Inhibition of AT1R and MR attenuates receptor activation and inhibits pro-fibrotic signaling. Activation of AT2R by Compound 21 or Ang II, or of MasR by Ang-(1–7), inhibits TGFβ fibrotic signaling and counteracts the effects of the classical RAAS pathway. Pirfenidone may both inhibit AT1R and activate MasR.