FIGURE 1.
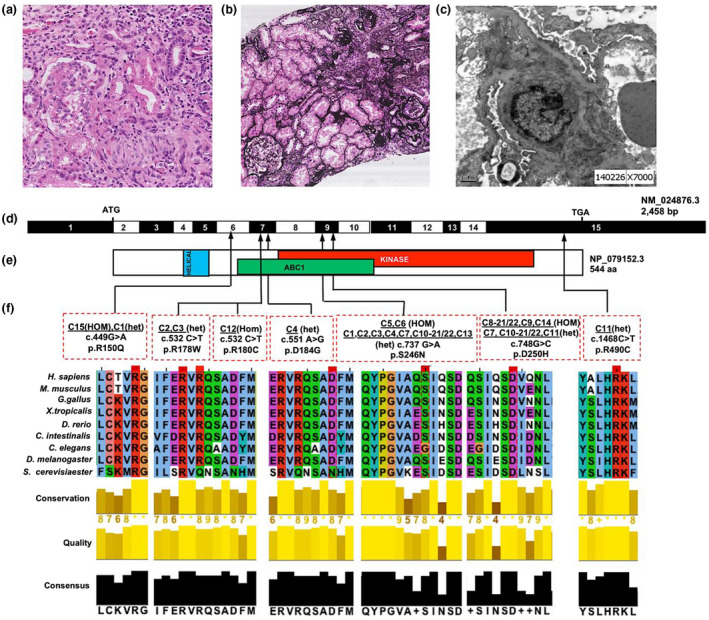
Exon capture and massively parallel sequencing reveal COQ8B mutations as causing SRNS and CKD. (a) Renal histology of individual C9 reveals FSGS by HE staining. (b) Renal histology of individual C9 shows FSGS and global glomerulosclerosis by Silver Jones Methenamine staining. (c) Renal histology of individual C9 shows foot process effacement. (d) Exon structure of human COQ8B cDNA. The COQ8B gene contains 15 exons. Positions of start codon (ATG) and of stop codon (TGA) are indicated. For the mutations detected (see f) arrows indicate positions in relation to exons and protein domains (see e). (e) Domain structure of the COQ8B protein. Extent of predicted domains, helical, ABC1, and kinase is depicted by colored bars, in relation to encoding exon position. (f) Nine different COQ8B mutations in 17 families with SRNS. Nucleotide change and amino acid changes (see Table S1) are given above sequence traces. Arrow heads denote altered nucleotides. Lines and arrows indicate positions of mutations in relation to exons (see d) and protein domains (see e). For the missense mutations, conservation across evolution of altered amino acid residues is shown. CKD, chronic kidney disease; FSGS, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
