Figure 4.
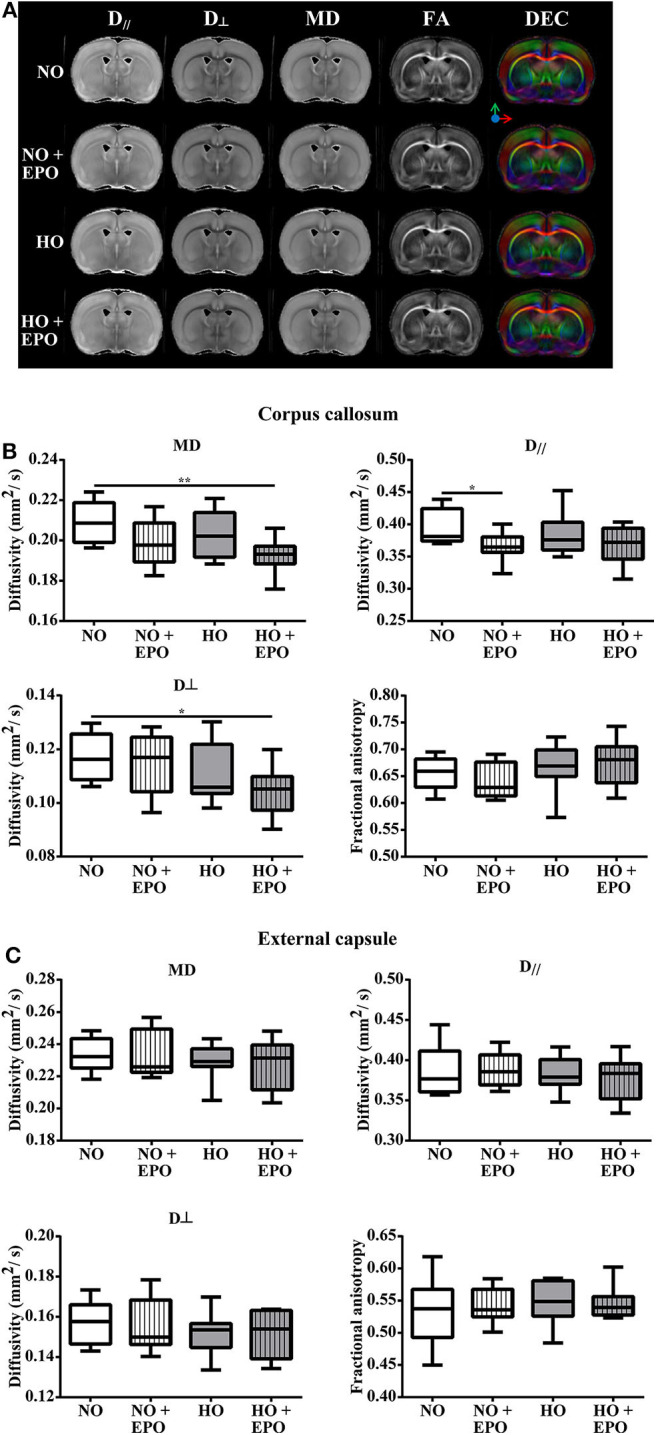
Long-term microstructural development after neonatal hyperoxia-induced brain-injury. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) was performed in 5 months old rats, which were exposed to behavior tests at the age of 2 and 4 months. From P3 to P5, rats were either exposed to normoxia [21% oxygen (NO)] or hyperoxia (80% oxygen (HO)] and treated with Epo (4 × 5000 IU/kg body weight per day from P3 to P6) or with an equal amount of normal saline. (A) For each treatment group, representative maps for axial diffusivity (AD, D//), radial diffusivity (RD, D⊥), mean diffusivity (MD), fractional anisotropy (FA) and direction encoded colour maps (DEC) derived from DTI are shown. Diffusivity values for MD, AD (D//), RD (D⊥) and FA are displayed for (B) corpus callosum, and (C) external capsule. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, n = 8 rats/group.
