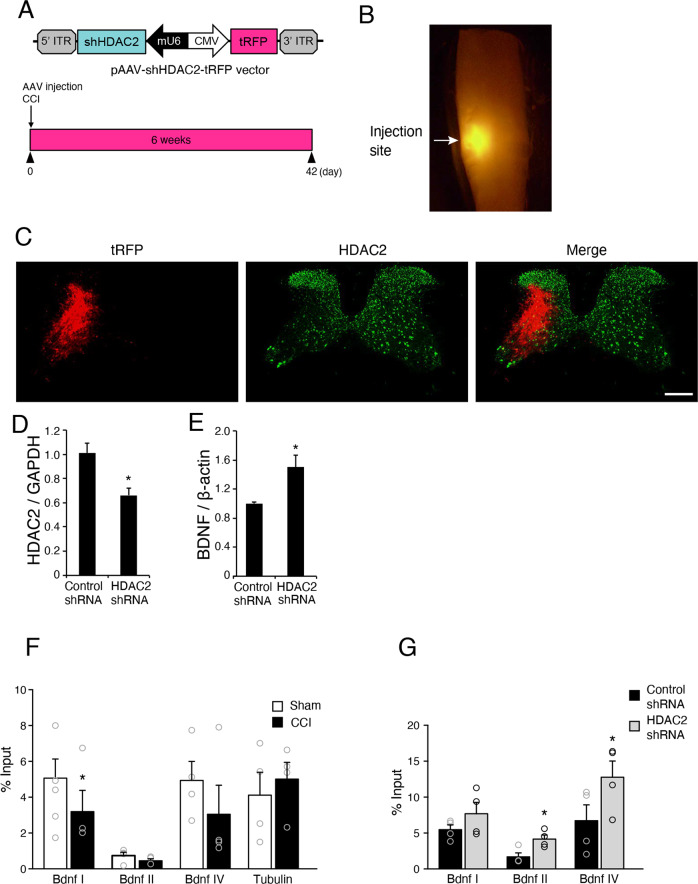
Fig. 7. AAV-mediated knockdown of HDAC2 increases BDNF expression following brain injury.
a Schematic images of AAV-HDAC2 shRNA plasmid construction and timeline of AAV injection in the cervical cord after CCI. b Representative images of the cervical spinal cord injected with AAV-shRNA-tRFP. c Representative images of transverse sections of the cervical spinal cord injected with AAV-HDAC2 shRNA stained with anti-HDAC2 antibodies. Scale bar: 200 μm. d Knockdown efficiency of HDAC2 shRNA in Chx10-GFP-positive neurons. Neuronal nuclei were isolated from tRFP-positive regions in the cervical spinal cord following INTACT method, and subjected to RNA extraction and real-time PCR. n = 4. *p < 0.05; Student′s t test. e BDNF expression is increased in Chx10-GFP-positive neurons injected with AAV-HDAC2 shRNA compared with control shRNA. n = 4. *p < 0.05; Student′s t test. f Brain injury induces hypoacetylation of H4K5 on BDNF promoter I but not on tubulin promoter in the denervated side of the spinal cord. n = 4. *p < 0.05; Student′s t test. g Injection of AAV-HDAC2 shRNA increases the acetylation of H4K5 on BDNF promoter II and IV following injury. n = 4. *p < 0.05; Student′s t test.