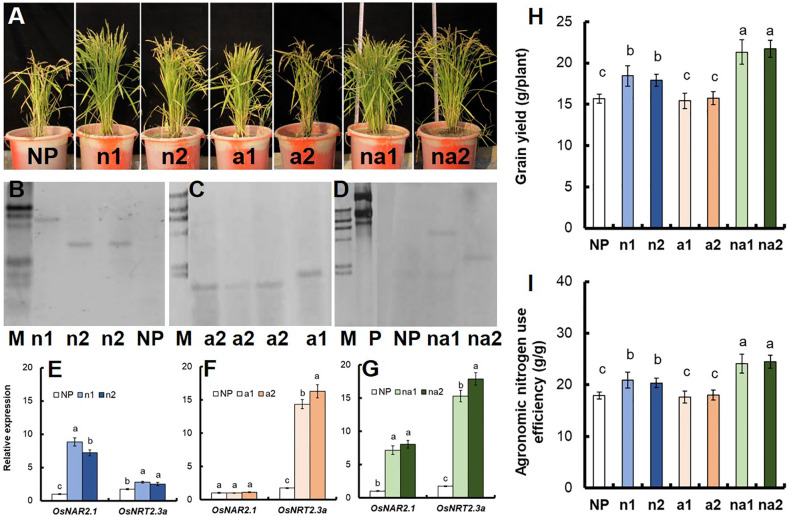
Figure 5.
Grain yield and agronomic nitrogen use efficiency of Nipponbare transgenic lines. (A) Phenotype of wild-type (cv. Nipponbare, NP), p35S:OsNAR2.1 transgenic lines (n1 and n2), p35S:OsNRT2.3a transgenic lines (a1 and a2), and p35S:OsNAR2.1-p35S:OsNRT2.3a transgenic lines (na1, na2). Southern blot analysis the copy number of (B) p35S:OsNAR2.1 transgenic lines, (C) p35S:OsNRT2.3a transgenic lines, and (D) p35S:OsNAR2.1-p35S:OsNRT2.3a transgenic lines. Genomic DNA isolated from T2 generation transgenic plants was digested with the Hind III and EcoR I restriction enzymes. A G418 gene probe was used for hybridization. P, positive control; M, marker. qRT-PCR analysis the expression of OsNAR2.1 and OsNRT2.3a of (E) p35S:OsNAR2.1 transgenic lines, (F) p35S:OsNRT2.3a transgenic lines, and (G) p35S:OsNAR2.1-p35S:OsNRT2.3a transgenic lines. RNA was extracted from culm. Comparison of (H) grain yield and (I) agronomic nitrogen use efficiency between the NP and transgenic lines. Error bars: SE (n = 3). The different letters indicate a significant difference between the transgenic line and the WT (P < 0.05, one-way ANOVA).