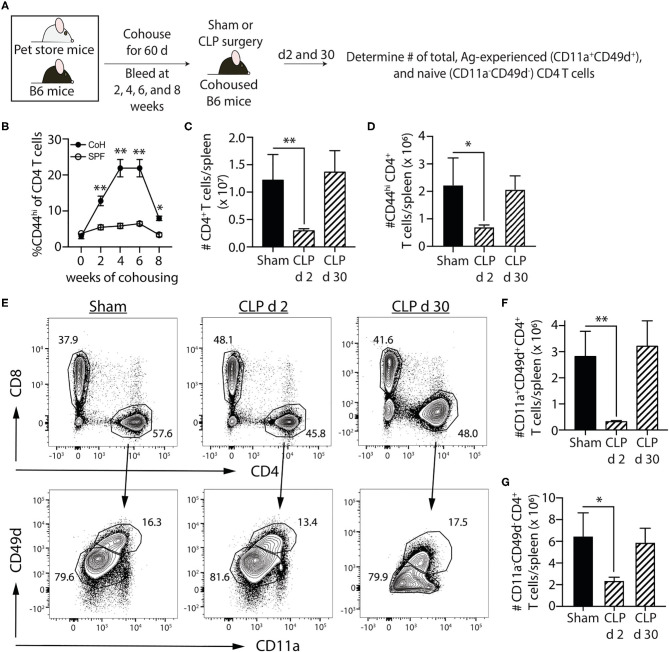
Figure 3.
Sepsis induces transient loss in number of pre-existing “Ag-experienced” CD4 T cells in microbially-experienced “dirty” mice. (A) Experimental design—SPF B6 mice were cohoused with pet store mice for 60 days to permit microbe transfer and immune system maturation. (B) Age-matched SPF and cohoused (CoH) mice were bled prior to and at 2, 4, 6, and 8 weeks after cohousing to determine the frequency of CD44hi CD4 T cells. (C–G) Sham or CLP surgery was performed on cohoused B6 mice. The number of total, CD44hi, CD11a+CD49d+ “Ag-experienced,” and CD11a−CD49d− naive CD4 T cells in the spleen was determined 2 and 30 days post-surgery by flow cytometry. (E) Representative flow plots show gating strategy. Positive and negative gating determined using FMO controls. The number of (C) total, (D) CD11a+CD49d+, and (E) CD11a−CD49d− CD4 T cells was determined. Data shown are representative of 2 independent experiments, with at least 4 mice/group in each experiment. *p ≤ 0.05 and **p ≤ 0.01.