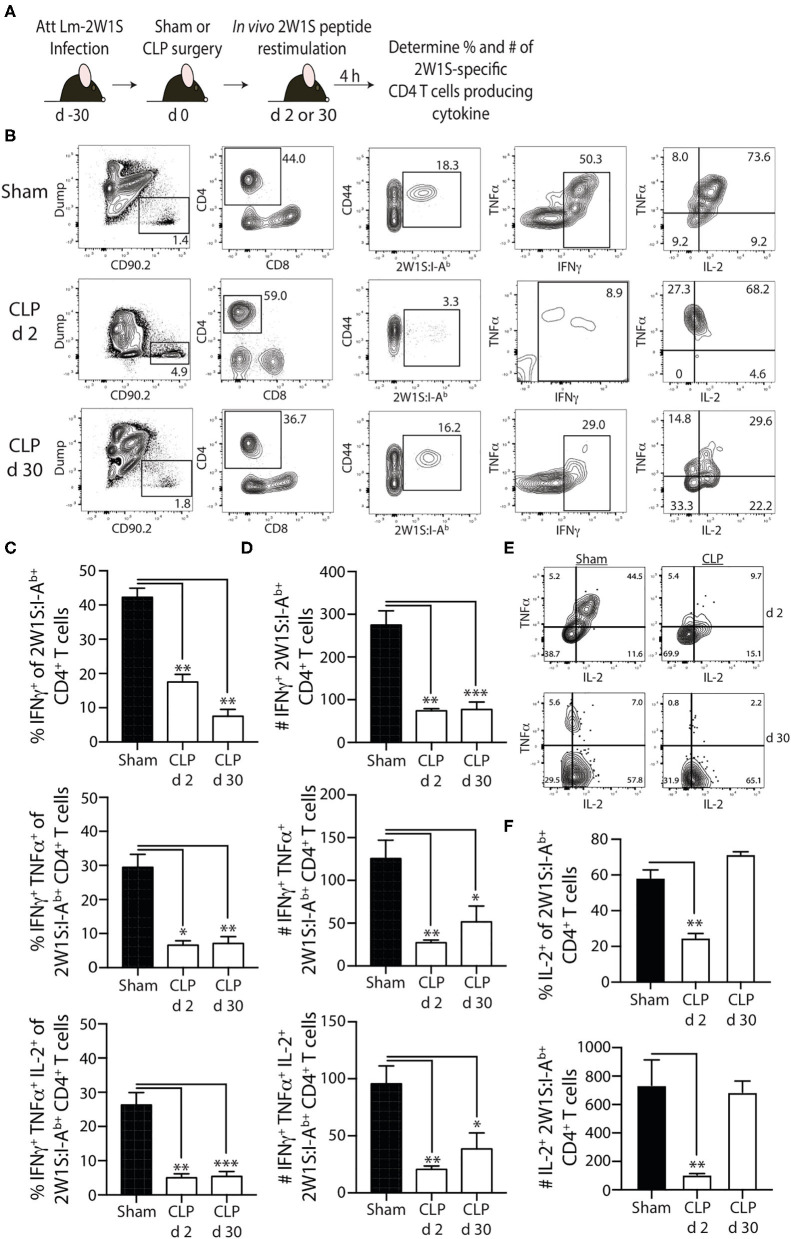
Figure 5.
Sepsis impairs the ability of 2W1S-specific memory CD4 T cells to produce effector cytokines after in vivo cognate Ag restimulation. (A) Experimental design—B6 mice were immunized with attenuated L. monocytogenes-2W1S (107 CFU i.v.) 30 days before sham or CLP surgery. Mice were injected with 2W1S peptide (100 μg i.v.) 2 or 30 days after surgery to restimulate the 2W1S-specific memory CD4 T cells. Spleens were harvested 4 h later, and the frequency and number of IFNγ+, IFNγ+TNFα+, and IFNγ+TNFα+IL-2+ 2W1S-specific CD4 T cells was determined by flow cytometry. (B) Representative flow plots of intracellular IFNγ, TNFα, and IL-2 detection in CD44hi2W1S:I-Ab+ CD4 T cells after in vivo peptide restimulation. Plots show cells gated from 2W:I-Ab-enriched CD4 T cells from sham- or CLP-treated mice. Positive and negative gating determined using FMO controls. Frequency (C) and number (D) of CD44hi2W1S:I-Ab+-specific CD4 T cells in the spleen producing IFNγ, IFNγ/TNFα, and IFNγ/TNFα/IL-2. (E) Representative flow plots of intracellular IL-2 detection in CD44hi2W1S:I-Ab+ CD4 T cells after in vivo peptide restimulation. Plots show cells gated from 2W:I-Ab-enriched CD4 T cells from sham- or CLP-treated mice. Positive and negative gating determined using FMO controls. (F) Frequency and number of CD44hi2W1S:I-Ab+-specific CD4 T cells in the spleen producing IL-2. Data shown are representative of 2 independent experiments, with at least 4 mice/group in each experiment. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, and ***p ≤ 0.005.