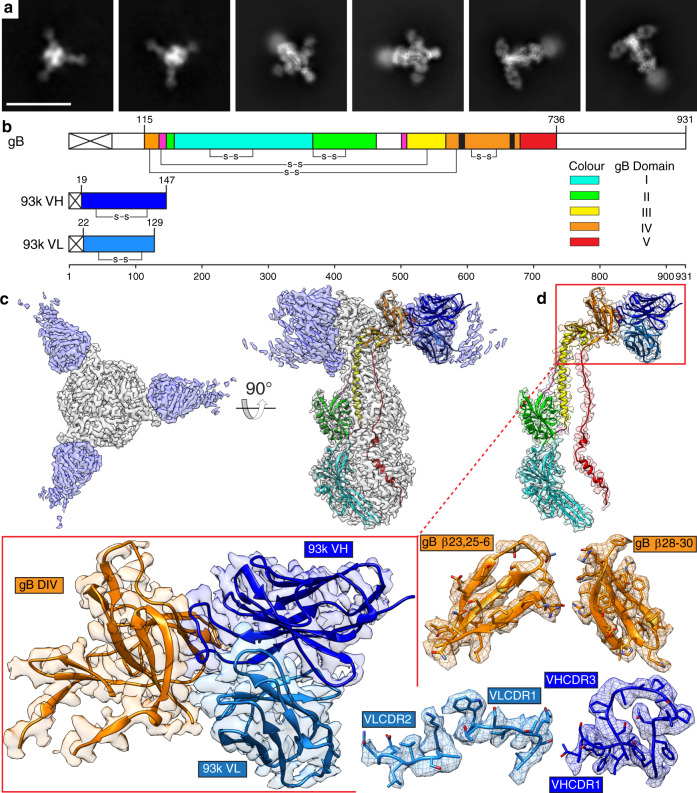
Fig. 2. Near atomic resolution cryo-EM structure of human neutralizing mAb 93k Fab fragments bound to native VZV gB.
a Representative 2D class averages used to generate the 2.8-Å cryo-EM structure of the gB-93k complex. Scale bar (white) 20 nm. b Linear maps of VZV gB, 93k VH and 93k VL, are drawn to scale and each domain colored accordingly: DI (cyan), DII (green), DIII (yellow), DIV (orange), DV (red), linker regions (hot pink), 93k VH (blue) and 93k VL (light blue). The predominant interaction sites of the 93k VHCDR3 loop at gB β23 and β30 are highligted in black on the gB linear structure. c Cryo-EM map of the VZV gB-93k complex. The gB trimer (gray) and the 93k Fab fragments (blue) are segmented (see Supplementary Movie 1). d Segmentation of the cryo-EM map for one VH and VL chain of a 93k Fab fragment bound to a protomer of VZV gB (See Supplementary Movie 1). The structures of VZV gB and 93k VH and VL are represented as ribbons. Expanded views of the cryo-EM map for gB DIV and the 93k VH and VL are highlighted by the red boxes with the structure represented by ribbons and the cryo-EM map desity shown. Segementation and amino acid sidechains are shown for the exploded view of gB DIV β-strands (β23, 25–26 and β28-30) and mAb 93k CDR loops (VHCDR1, VHCDR3, VLCDR1, and VLCDR2) that form the gB-93k interface (see Supplementary Movie 2).