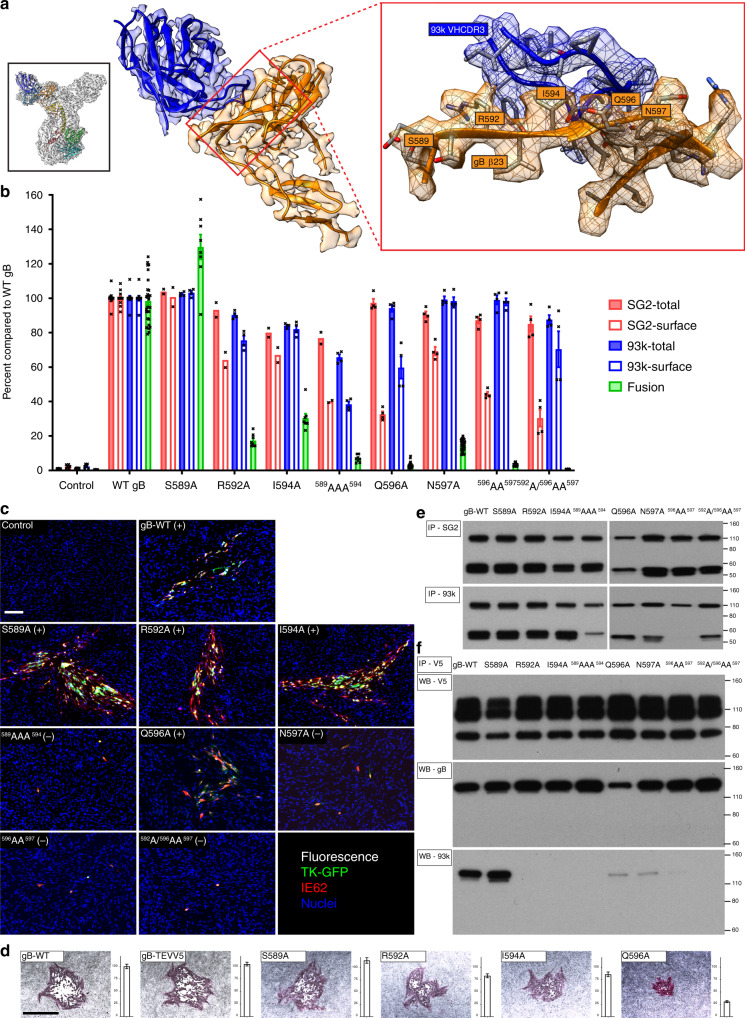
Fig. 5. Domain IV β23 residues are critical for fusion function and VZV replication.
a Near atomic structure of the mAb 93k binding site at VZV gB β23. The orientation of the complete gB-93k Fab map is shown in the small box in the top left-hand corner colored as for Fig. 1e. A portion of the cryo-EM map for gB domain IV chain A (Orange) and the bound 93k Fab (Blue) are shown. The red box on the right is a magnified view of β23 with the amino acid side chains on VZV gB shown and those subjected to mutagenesis labeled. b Quantification of total and cell surface levels of gB DIV mutants produced by transfected CHOs and their capacity for cell–cell fusion measured by the SRFA. All values are normalized as a percentage to WT gB. Bar charts represent n = 4 (n = 2 for SG2 staining of S589A, R592A, I594A, and 589AAA594) samples for total and cell surface gB detected using mAbs SG2 and 93k, and n = 28 (n = 8 for S589A, R592A, I594A, and 589AAA594) samples for fusion examined over two independent experiments. Error bars represent ±SEM. c Immunofluorescence of MeWo cells at 72 h post transfection with pOka-BACs with gB mutations. Melanoma cells were transfected with pOka-TK-GFP BACs carrying alanine substitution S589A, R592A, I594A, 589AAA594, Q596A, N597A, 596AA597, and 592A/596AA597. The (+) or (−) indicate whether or not virus was recovered from the transfections. Immunofluorescence staining was performed for IE62 as a marker for early infection because the TK-GFP is a late protein product during VZV replication. Scale bar (white) 100 µm. d Immunohistochemistry staining of plaques and their sizes for the pOka-TK-GFP gB, pOka-TK-GFP gB-TEVV5, and β23 mutants S589A, R592A, I594A, and Q596A. Scale bar (black) 1 mm. Bar charts represent n = 40 plaques measured over two independent experiments (Supplementary Data 2). All values were normalized to WT VZV. Error bars represent ±SEM. e Immunoprecipitation of the VZV gB β23 mutants from transfected CHO cells using anti gB mAbs SG2 and 93k, and western blot with anti-gB Ab 746–868. The gH control lane where CHO cells were transfected with gH-WT is shown in Fig. 6e. f Reducing SDS–PAGE and western blot of gB co-immunoprecipitated with gH-V5 from CHO cells transfected with the β23 mutants, gH-V5 and gL. The gB-WT control lane using the gH-WT negative control is shown in Fig. 6f. Western blots were performed using mAb to V5 (Top), anti-gB Ab 746–868 (middle), and a mAb 93k (bottom). e, f Numbers to the right of the blots are molecular weight standards (kDa). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.