Figure 2.
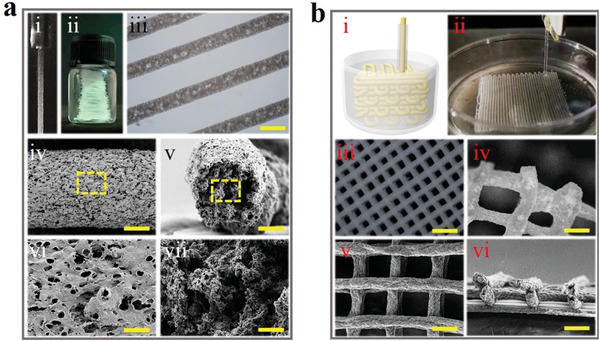
a) PU microfiber generated from microfluidics. i) Online spinning process of the microfiber. ii) Digital image of continuous microfibers in a vessel. iii) Optical microscopic image of the PU microfiber. iv–vii) SEM images of PU microfiber at iv) surface and v) cross section, and the magnified field of vi) surface as well as vii) cross section. Scale bars are iii) 200 µm, iv,v) 50 µm, vi,vii) 5 µm. b) 3D‐structured slippery PU textile. i) Schematic 3D printing fabrication process. ii) Digital image of the generating process. iii,iv) Optical microscopic image of iii) the overall morphology of PU textile and iv) its connection region. v,vi) SEM images of PU textile at v) surface and vi) cross section. Scale bars are iii) 1 mm and iv–vi) 200 µm.
