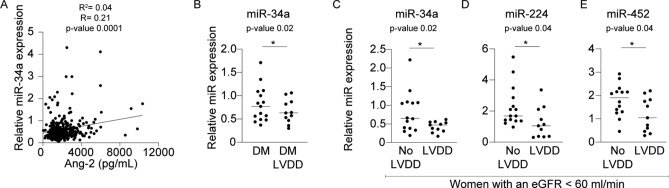
Figure 2.
Plasma Ang-2 levels and circulating miR-34a, -224 and -452 in (female) DM patients with LVDD compared controls. (A) Particularly miR-34a displayed a significant correlation with Ang-2 in the total patient population of patients with LVDD (N = 366, R2 0.04, R = 0.21, p = 0.001, 95% CI 0.103–0.312). (B) Lower levels of miR-34a in diabetic patients with LVDD compared to diabetic patients without LVDD (Fold change 1.2, p = 0.02, 95% CI − 0.428 to 0.117). (C) Lower levels of miR-34a, in women with an eGFR < 60 ml/min and LVDD compared to women without LVDD (Fold change 1.9, p = 0.03, CI − 0.737 to − 0.030). (D) Decreased plasma miR-224 in women with an eGFR < 60 ml/min and LVDD compared to women without LVDD (Fold change 1.8, p = 0.04, CI − 1.998 to − 0.059) and (E) decreased miR-452 in women with an eGFR < 60 ml/min and LVDD compared to women without LVDD (Fold change 1.5, p = 0.04, CI − 1.213 to − 0.039). Relative miR-expression values are normalized to plasma miR-16 levels, presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) and group differences are depicted as *p ≤ 0.05. Correlations between variables were calculated using the Spearman rank correlation.