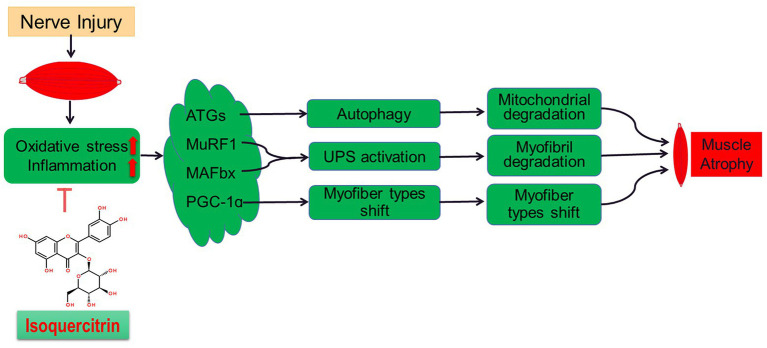
Figure 7.
A schematic diagram illustrating the proposed mechanism by which peripheral nerve injury induces soleus muscle atrophy. Denervation-induced skeletal muscle atrophy is associated with oxidative stress and inflammation. The inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation through Isoquercitrin alleviated denervation-induced skeletal muscle atrophy by reducing proteolysis, inhibiting mitophagy, and reversing the slow-to-fast fiber type conversion following denervation.