Figure 4.
Cholesterol Dehydrogenase-Encoding Gut Bacteria Are Uncultured Members of Cluster IV Clostridium and Are Prevalent Across Geographically Diverse Human Populations
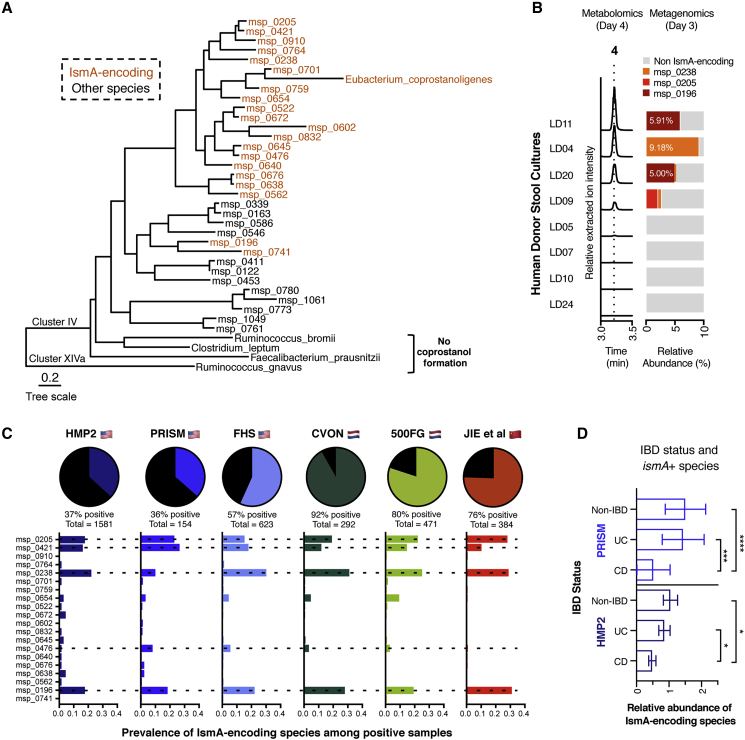
(A) 20 different MSPs containing ismA genes could be identified in human gut microbiome datasets. Phylogenetic tree was generated using PhyloPhlAn and includes all IsmA-encoding MSPs as well as species in the direct neighborhood or marker species for Clostridium cluster IV and cluster XIVa.
(B) Ex vivo conversion of cholesterol to coprostanol by human fecal samples. Coprostanol formation occurred in 4 of the 8 samples cultured in basal cholesterol medium, with all 4 metabolizing samples containing at least one of the IsmA-encoding species identified at day 3.
(C) Proportion of microbiome samples within each respective cohort that contains at least one IsmA-encoding species. IsmA-encoding species msp_0205, msp_0421, msp_0238, and msp_0196 are the most abundant across all of the populations examined. Dotted lines show species whose IsmA proteins have been shown to metabolize cholesterol in vitro.
(D) Relative abundance levels of IsmA-encoding species present in the gut microbiome when stratified by disease state (HMP2: total, n = 1,581; non-IBD, n = 411, avg rel. ab. = 1.047; UC, n = 437, avg rel. ab. = 0.8613; CD, n = 733, avg rel. ab. = 0.4864; non-IBD versus UC p = 0.72; non-IBD versus CD p = 0.009; UC versus CD p = 0.009; PRISM: total, n = 154; non-IBD, n = 34, avg rel. ab. = 1.51; UC, n = 52, avg rel. ab. = 1.437; CD, n = 68, avg rel. ab. = 0.525; non-IBD versus UC p = 0.14; non-IBD versus CD p = 1.33e−6; UC versus CD p = 6.30e−4). p values were determined by a Wald test for PRISM (a linear model) and a Satterthwaite's method for HMP2 (a mixed linear model with random effect for subjects) and corrected for multiple comparisons with Benjamini-Hochberg method. The center bar represents the mean and error bars representing 95% CIs.