Table 7.
P-gp modulating activity of flavone derivatives 80–84 on K562/DOX cells [114].
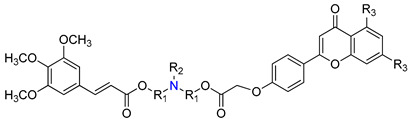
| Compound | R1 | R2 | R3 | [I]0.5 (µM) 1 | αmax 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80 | (CH2)5 | CH3 | OH | 0.96 | 0.99 |
| 81 | (CH2)5 | CH3 | H | 0.34 | 0.99 |
| 82 | (CH2)5 |
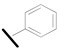
|
H | 0.43 | 0.99 |
| 83 | (CH2)5 | H | H | 1.32 | 0.69 |
| 84 | (CH2)2O(CH2)2 | CH3 | H | 1.23 | 0.86 |
| Verapamil (1) | - | - | - | 1.60 | 0.70 |
1 [I]0.5 represents the concentration that causes a half-maximal increase (a = 0.5) in the nuclear concentration of pirarubicin and measures the potency of the modulator. Lower [I]0.5 values mean stronger P-gp modulators; 2 αmax represents the efficacy of the modulator and is the maximum increase in the nuclear concentration of pirarubicin in resistant cells that can be obtained with a given compound. The value of αmax varies between 0 (in the absence of the inhibitor) and 1 (when the amount of pirarubicin in resistant cells is the same as in sensitive cells).
