Table 13.
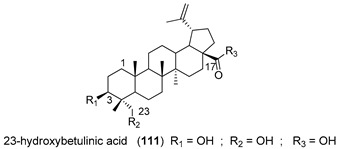
| Compound | R1 | R2 | R3 | Cells/In Vivo Models | Biological Activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 112 | OH |
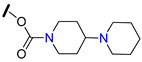
|
OH | HepG2/ADM | At 5 µM reduced the GI50
1 of vincristine 132-fold and paclitaxel 79-fold. Suppressed P-gp efflux function. Inhibition of ERK1/2 and AKT phosphorylation. |
| MCF-7/ADR | At 5 µM reduced the GI50 1 of vincristine 151.04-fold and paclitaxel 151.07-fold. | ||||
| KB-C2 cell xenografts in nude mice model | At 15 mg/kg significantly enhanced the anticancer activity of paclitaxel (18 mg/kg), with no significant change in the body weight (Reduced toxicity). | ||||
| 113 | OH | OH |
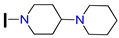
|
HepG2/ADM | At 4 µM reduced the GI50 1 of vincristine 48.03–fold and paclitaxel 82-fold. Inhibited P-gp ATP-ase activity and suppress its efflux function |
| MCF-7/ADR | At 4 µM reduced the GI50 1 of vincristine 29-fold and paclitaxel 47-fold. | ||||
| 114 | OAc | OAc |

|
HepG2/ADM | At 4 µM reduced the GI50 1 of vincristine 232-fold and paclitaxel 282-fold. Inhibited P-gp ATP-ase activity and suppress its efflux function. |
| MCF-7/ADR | At 4 µM reduced the GI50 1 of vincristine 183-fold and paclitaxel 59-fold. | ||||
| verapamil (1)2 | - | - | - | HepG2/ADM | At 5 µM reduced the GI50 1 of vincristine 22-fold and paclitaxel 11-fold. |
| MCF-7/ADR | At 5 µM reduced the GI50 1 of vincristine 29-fold and paclitaxel 59-fold. |
1 GI50—Defined as the concentration of compound that inhibited cell growth by 50%. Lower GI50 values mean higher intrinsic toxicity; 2 verapamil (1) was used as positive control.
