FIGURE 1.
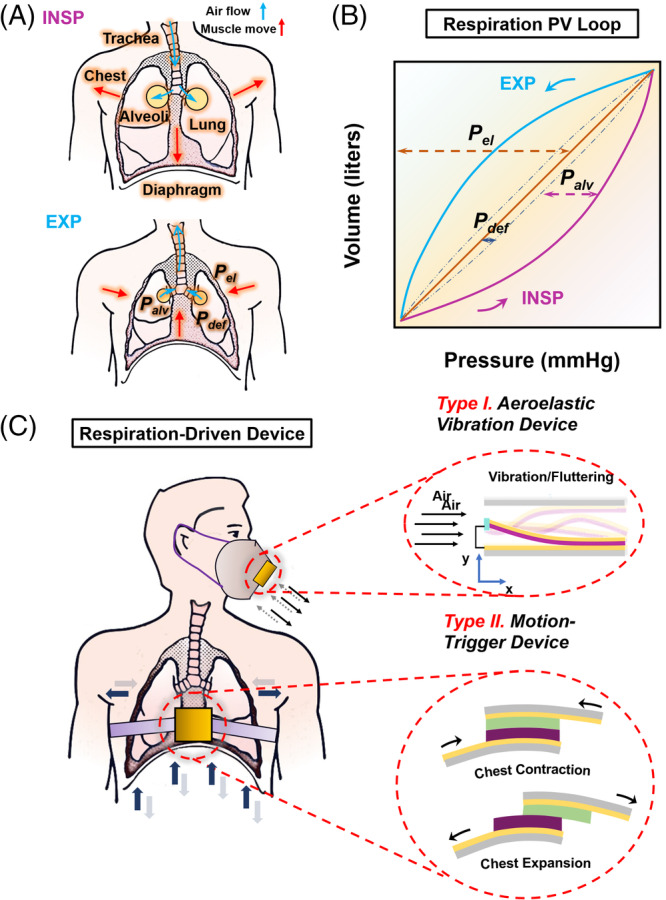
Mechanics of respiration. A, Schematics of muscle movement and air flow during inspiration (upper image) and expiration (bottom image). B, Typical pressure‐volume loop (one respiratory cycle) during breathing. P el, P def, and P alv are represented by the abscissal distance from the axis of ordinates to the diagonal, from the diagonal to the dashed curve, and from the dashed curve to the loop, respectively. C, Schematics of two main types of respiration‐driven TENG that harvest energy from respiration at different locations. TENG, triboelectric nanogenerator
