FIGURE 1.
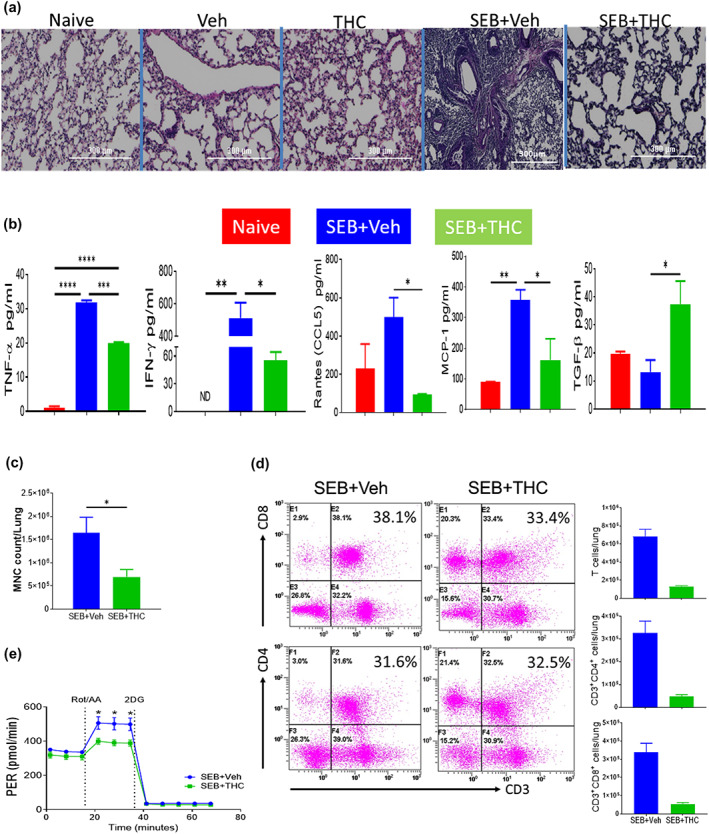
Effect of Δ9‐tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) on lung inflammation in staphylococcal enterotoxin‐B (SEB)‐induced acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). C3H mice were injected with SEB followed by THC or vehicle as described in Section 2. Representative images of histopathological H&E staining sections of excised lung tissues in low power (4×) were shown (a). elisa was used in the measurement of serum cytokines and chemokines (b). The change in total number of mononuclear cells isolated from the lungs was shown (c). Flow cytometry was used in the analysis of changes of CD3+, CD3+CD4+ and CD3+CD8+ T cells in the lung‐associated mononuclear cells from ARDS mice after THC treatment and a statistical bar graph is on the right of the flow (d). The inhibitory effect of THC on the proton efflux rate (PER) on CD3+ T cells (e). Vertical bars represent data expressed as mean ± SEM with five mice in each group. P‐value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant, * P < 0.05
