Figure 1.
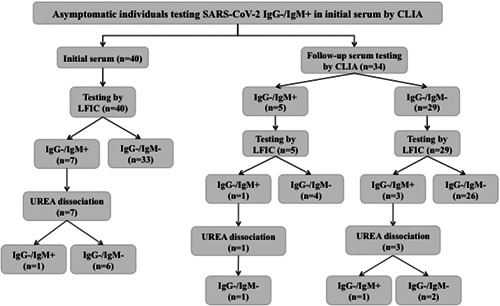
Flow chart depicting the results of analyses of sera from asymptomatic health care workers displaying a SARS‐CoV‐2 IgM+/IgG− antibody pattern on initial screening by a chemiluminescent immunoassay (MAGLUMI 2019‐nCov IgG/IgM CLIA; Snibe, Shenzhen, China) (n = 40). Qualitative assessment of SARS‐CoV‐2 IgM avidity was carried out using the LFIC AllTest 2019‐nCoV IgG/IgM Rapid Test Cassette (Hangzhou AllTest Biotech Co, Ltd, Hangzhou, China). A volume of 10 µL of serum was diluted into 1 mL of sample buffer before depositing (100 µL) into the appropriate location of the cassette (Test T‐hole). When the fluid was about to reach the absorbent pad, 100 µL of sample buffer containing 6 M urea was added to the T hole on the card. Serum specimens were run in parallel in the absence of urea treatment. Each reading was carried out independently by two observers after 20 minutes incubation. Appearance of either strong or weak sharp bands at the T line was recorded as a positive result. Absence of discernible lines was recorded as negative. Complete disappearance of reactive lines after urea treatment was interpreted as presence of low‐avidity antibodies, whereas their persistence was taken to indicate high‐avidity antibody presence
