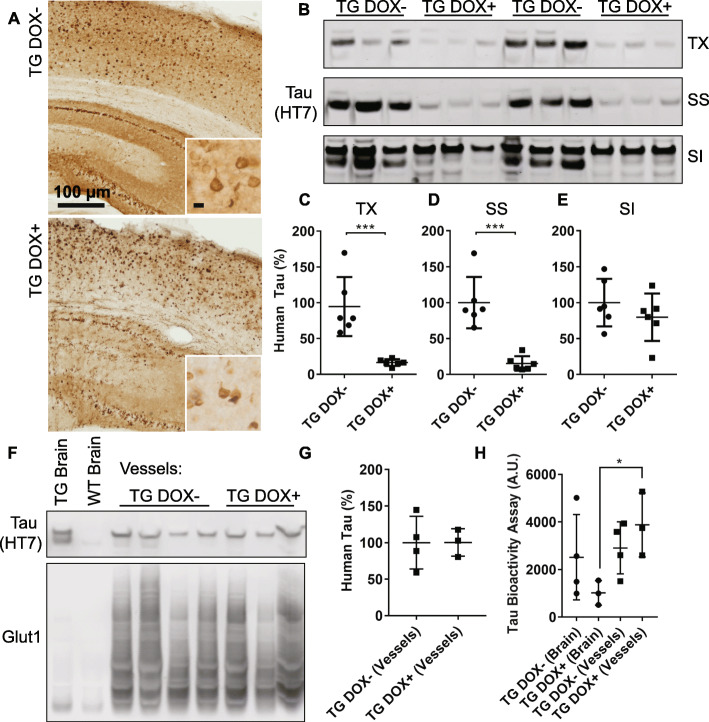
Fig. 3.
Doxycycline treatment reduces soluble tau but does not alter vascular tau. a Sections from rTg4510 mice (TG) with and without doxycycline treatment were labeled for tau protein (HT7) showing a significant reduction in tau outside of neurofibrillary tangles. Insets show higher magnification images of cortical pathology. Scale bar = 10 μm. b Western blotting of human tau (HT7) present in Triton X (TX), sarkosyl soluble (SS) and sarkosyl insoluble (SI) fractions from a protein insolubility assay. c Quantification of western blots confirms reduced soluble tau present in TX (Student’s t test, p = 0.001) and (d) SS fractions (p = 0.0002) and (e) no change in SI fractions (p = 0.31). Tau measures were normalized to a total protein stain to control for loading differences, which can be found along with uncropped blots in the supplement. f Western blotting of human tau in brain and isolated brain vessels from doxycycline treated (+) and untreated (−) mice. Glut1 is included to show enrichment of endothelial protein in vessels preparations. g Quantification of total human tau in vessels normalized to Glut1. h A biosensor cell assay shows retained tau bioactivity in transgenic blood vessels from Dox + mice (Repeated Measures ANOVA, Sidak’s post hoc p = 0.04) and no difference in Dox- mice (p = 0.89). All graphs are plotted with means +/− standard deviations. * indicates p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001