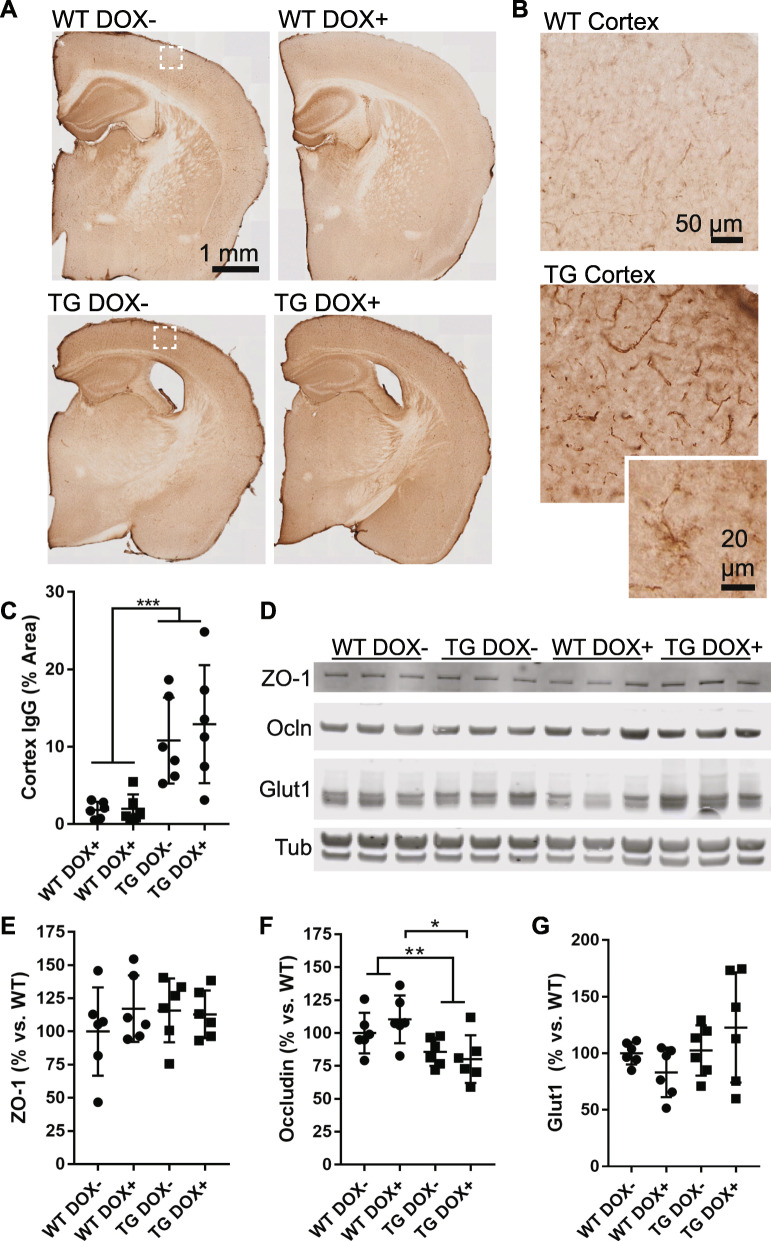
Fig. 6.
Compromised blood brain barrier function is not restored in tau expressing mice. a Sections from wild-type (WT) and transgenic (TG) mice were labeled to detect mouse IgG, which is normally excluded from the brain or found only within vascular lumens. b Enlarged views of boxes from (a) show that mouse IgG was detected in both wild-type and transgenic cortex, but to a greater extent in transgenic mice, including within vascular walls and in cells with glial morphology (inset). c A threshold-based quantification of cortical IgG labeling shows an increased in transgenic mice (Two-way ANOVA, genotype p < 0.0001, treatment p = 0.06). d A Western blot of tight junction proteins ZO-1 and Occludin (Ocln) as well as Glut1 (endothelial cell marker) and tubulin (loading control). e Quantification of the western blot from (d) showing ZO-1 protein normalized to Glut1 amount. Results are shown as the percentage versus wild-type (Dox-). No difference was seen in ZO-1 (Two-way ANOVA, genotype p = 0.59, treatment p = 0.50). f Quantification of Occludin normalized to Glut1 revealed a decrease in transgenic mice (Two-way ANOVA, genotype p = 0.003, treatment p = 0.71) including a significant difference between WT DOX+ and TG DOX+ (Sidak’s multiple comparison, p = 0.02). g Total vascular protein loaded on the Western blot was not significantly different between groups and is plotted normalized to tubulin (Two-way ANOVA, genotype p = 0.09, treatment p = 0.89)