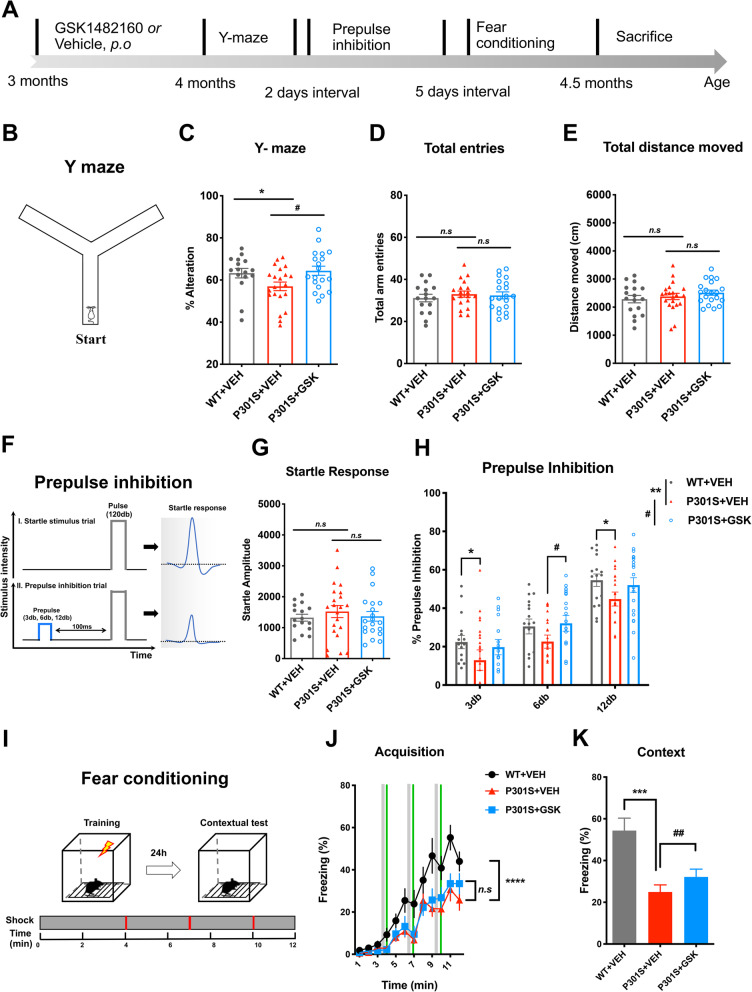
Fig. 4.
Behavioral testing of P301S mice after GSK1482160 treatment. a. Schematic diagram of behavioral tests. b-e. Schematic diagram of Y-maze (b). Percentage of spontaneous alternation (c), number of total arm entries (d) and total distance moved during tests (e) in Y-maze. *p < 0.05, P301S + VEH vs. WT + VEH; #p < 0.05, P301S + GSK vs. P301S + VEH as determined by one-way ANOVA (alpha = 0.05) with Dunnett’s post-hoc. n = (17, 21, 20) mice for WT + VEH, P301S + VEH and P301S + GSK groups. Graphs indicate mean ± s.e.m. f and g. Schematic diagram of pre-pulse inhibition test (f). Acoustic startle amplitude as measured in trials with 120 db without a pre-pulse (g). PPI (%) at three different pre-pulse intensities (3, 6 and 12 db above 65db background) (H). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, P301S + VEH vs. WT + VEH; #p < 0.05, P301S + GSK vs. P301S + VEH, n.s denotes no significance, as determined by two-way ANOVA (alpha = 0.05) and Bonferroni’s post-hoc. n = (17, 21, 20) mice for WT + VEH, P301S + VEH and P301S + GSK groups. i-k. Schematic diagram of fear conditioning (i). j. Percentage of freezing time of each minute during cued fear acquisition. ****p < 0.0001, P301S + VEH vs. WT + VEH as determined by two-way ANOVA (alpha = 0.05) and Bonferroni’s post-hoc. n = (17, 21, 20) mice for WT, P301S + VEH and P301S + GSK groups. k. % freezing during contextual text. ***p < 0.001, P301S + VEH vs. WT + VEH; ##p < 0.01, P301S + GSK vs. P301S + VEH as determined by paired Student’s t-test at each minute during the 5 min period. Graphs indicate mean ± s.e.m.