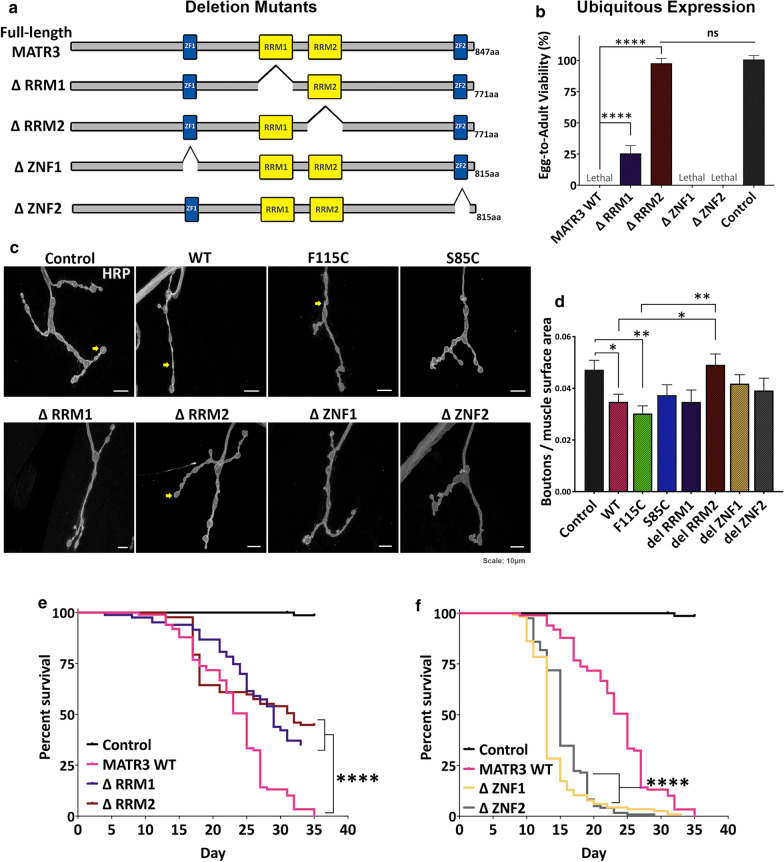
Fig. 3.
MATR3 toxicity is mediated through its RNA-binding domains. a Schematic diagram of MATR3 protein domain architecture in deletion mutant-transgenic flies, where each of the known functional domains are deleted. b Quantification of egg-to-adult viability in flies ubiquitously expressing MATR3 deletion mutants, driven by Tub-Gal4 driver. Constitutive ubiquitous expression of MATR3 deletion mutants showed partial rescue by ΔRRM1 and complete rescue by ΔRRM2 (n = 3, One-way ANOVA). c Representative immunofluorescence images of third-instar larval neuromuscular junction (NMJ) immunostained for presynaptic marker, HRP. Yellow arrows point to the synaptic boutons. d Quantification of number of synaptic boutons, normalized to surface area, showed that ΔRRM2 restored number of synaptic boutons back to near-control levels (n = 8, One-way ANOVA). e Kaplan–Meier survival curve of adults ubiquitously expressing MATR3 deletion mutants under the conditional driver. Both ΔRRM1 and ΔRRM2 significantly extended MATR3 lifespan, while f ΔZNF1 and ΔZNF2 further reduced MATR3 lifespan (n = 100, Log-rank Mantel-Cox test) Error bars indicate S.E.M. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ****p < 0.0001