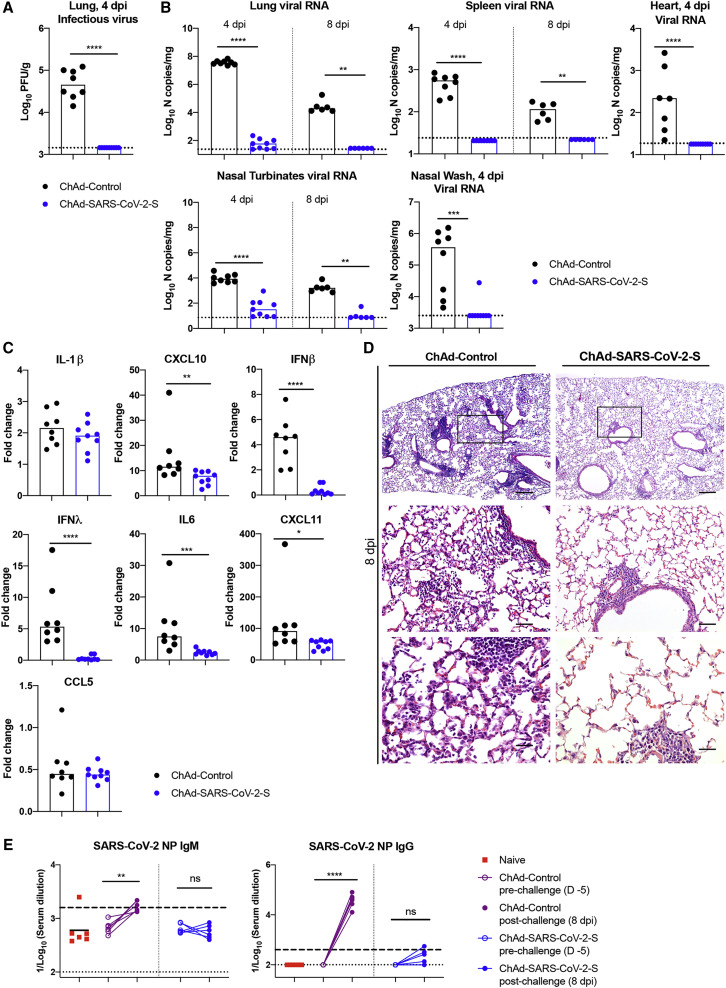
Figure 5.
Single-Dose Intranasal Immunization with ChAd-SARS-CoV-2-S Protects against SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Five-week-old BALB/c female mice were immunized with ChAd-control or ChAd-SARS-CoV-2-S via an intranasal route. On day 35 post-immunization, mice were challenged as follows: animals were treated with anti-Ifnar1 mAb and transduced with Hu-AdV5-hACE2 via the intranasal route 1 day later. Five days later, mice were challenged intranasally with 4 × 105 FFUs of SARS-CoV-2.
(A–C) Tissues and nasal washes were collected at 4 and 8 dpi for analysis. Infectious virus in the lung was measured by plaque assay (A). Viral RNA levels in the lung, spleen, heart, nasal turbinates, and nasal washes were measured at 4 and 8 dpi by qRT-PCR (B). Fold change in gene expression of indicated cytokines and chemokines was determined by qRT-PCR, normalized to Gapdh, and compared to naive controls in lung homogenates at 4 dpi (C; 2 experiments, n = 6–9; median values are shown). Columns show median values, and dotted lines indicate the LOD of the assays.
(D) Lungs were harvested at 8 dpi. Sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin and imaged at 40× (left; scale bar, 250 μm), 200× (middle; scale bar, 50 μm), and 400× (right; scale bar, 25 μm) magnifications. Each image is representative of a group of 3 mice.
(E) An ELISA measured anti-SARS-CoV-2 NP IgM (left) and IgG (right) antibody responses in paired sera obtained 5 days before and 8 days after SARS-CoV-2 challenge of ChAd-control or ChAd-SARS-CoV-2-S mice vaccinated by an intranasal route (n = 6). Dotted lines represent the LOD of the assay. Dashed lines indicate the mark for a 4-fold increase of pre-boost IgM and IgG levels.
For (A)–(C): Mann-Whitney test: ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; for (E): ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; paired t test. See Figures S4 and S5.