Figure 7.
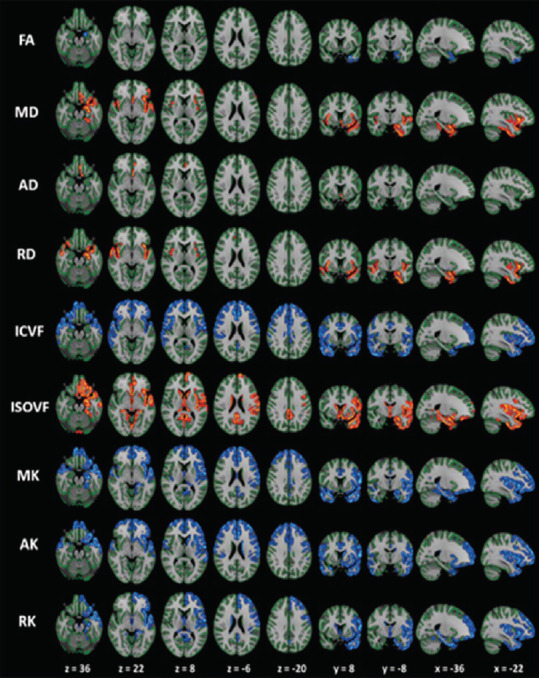
The gray-matter based spatial statistics (GBSS) analysis of diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), diffusional kurtosis imaging, and neurite orientation dispersion, and density imaging metrics in patients with Parkinson's disease (PD) versus controls.
Patients with PD demonstrated reduced FA, ICVF, MK, AK, and RK (highlighted in blue-light blue colors) and increased MD, AD, RD, and ISOVF (highlighted in red-yellow colors) compared with the agematched healthy subjects. In patients with PD, the changes of ICVF, MK, AK, and RK were measured in the limbic, paralimbic, frontal, and temporal cortical gray matter. The changes in the conventional DTI parameters (FA, AD, and RD) were noticeably smaller than those in MK, AK, RK, and ICVF. The results are enhanced (corrected P < 0.05) for visualization using using the fill script implemented in FSL. AD: Axial diffusivity; AK: axial kurtosis; FA: fractional anisotropy; ICVF: intracellular volume fraction; ISOVF: isotropic volume fraction; MD: mean diffusivity; MK: mean kurtosis; OD: orientation dispersion index; RD: radial diffusivity; RK: radial kurtosis. Reproduced with permission from Kamagata et al., 2017.
