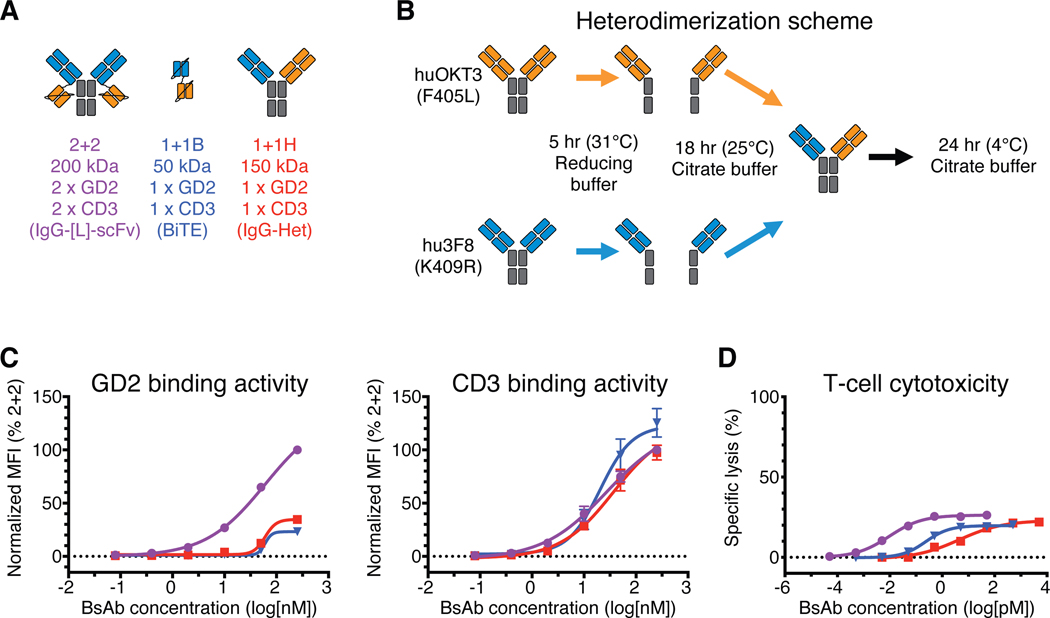
Fig. 1.
In vitro comparison of IgG-[L]-scFv to common BsAb designs
(A) Schematic of BsAb panel: IgG-[L]-scFv (2+2), BiTE (1+1B), and IgG-heterodimer (1+1H). Orange domains represent anti-huCD3ε domains (derived from huOKT3) and blue domains represent anti-GD2 domains (derived from hu3F8). (B) Schematic of the IgG heterodimerization by controlled Fab Arm Exchange. (C) Representative cell-binding activity of each BsAb against GD2(+) human M14 melanoma cells (left) and CD3(+) activated human T cells (right), measured by flow cytometry. Geometric mean intensity was normalized to 2+2 (100%) for each BsAb. (D) Representative T cell-dependent cytotoxicity for each BsAb. For reference: 2+2 is purple, 1+1B is blue, and 1+1H is red. Each curve represents one BsAb, and each point represents a single concentration, with two (FACS) or three (cytotoxicity) technical replicates. Data are shown as means ± standard deviation.