Fig. 3. Molecular contacts in the Vps24 filaments.
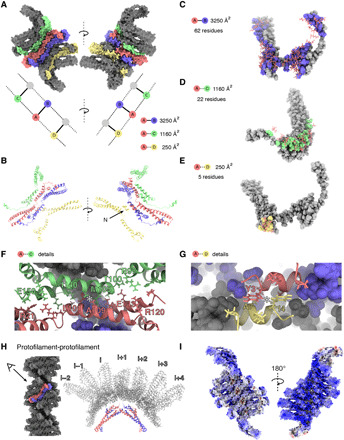
(A) Contacts between different Vps24 molecules within the filament. Space-filling representation of central blue-red dimer makes contacts to upper (green) and lower (yellow) neighbors. (B) One Vps24 molecule (red) with neighboring Vps24 molecules in ribbon presentation [color code as in (A)]. (C) Molecular residue contacts within a domain-swapped dimer. (D) Residue contacts between domain-swapped dimers and upper Vps24 neighbor. (E) Residue contacts between domain-swapped dimer and lower Vps24 neighbor. (F) Detailed view of the interface in (D) with an antiparallel alignment of residues M105-A109 centered by the asterisk. (G) Detailed view of contacting N termini shows antiparallel alignment of hydrophobic residues at asterisk. (H) Contacts between one domain-swapped dimer and seven dimers of the opposing strand are very scarce, resulting in a partial cavity. (I) Electrostatic potential map colored in units of kBT/e− with red as −10 and blue as 10 shows the strong positive charge on the inner side of a single strand.
