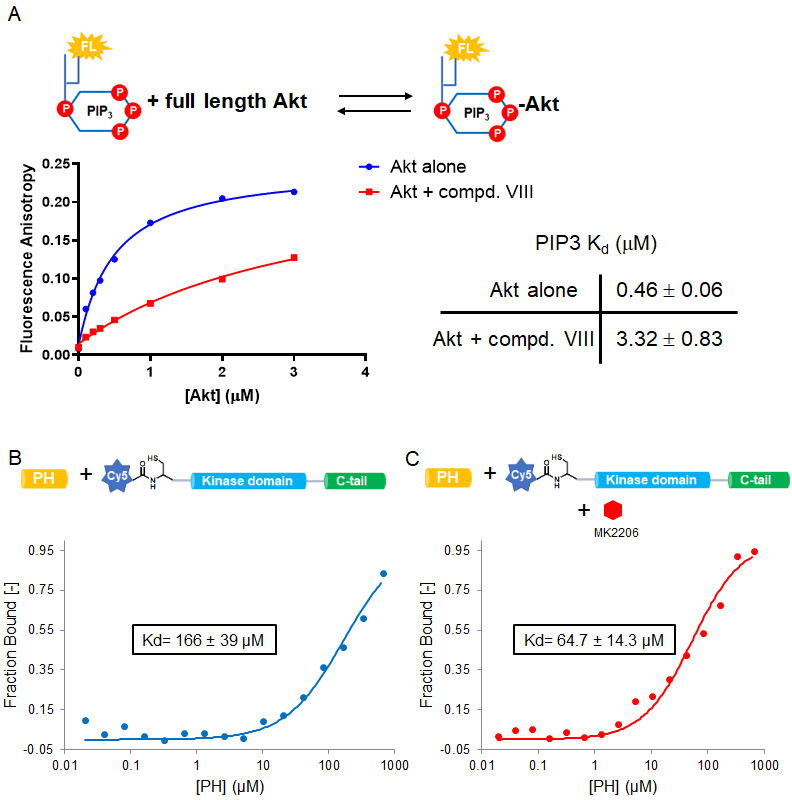
Figure 7. The allosteric drug-induced Akt inhibited form is distinct from its native autoinhibited form.
(A) Binding assays of phospholipid PIP3 with full-length Akt in presence of 20 µM MK2206. Chemical structure of MK2206 is shown on the right. The fluorescence anisotropy measurements (n = 2) were carried out and fit to quadratic binding isotherms, and Kd values shown ± S.D. (B) Cartoon model illustrated the distinct conformational structure of PH domain of allosteric drug-bound Akt when compared to that of natural autoinhibited form.
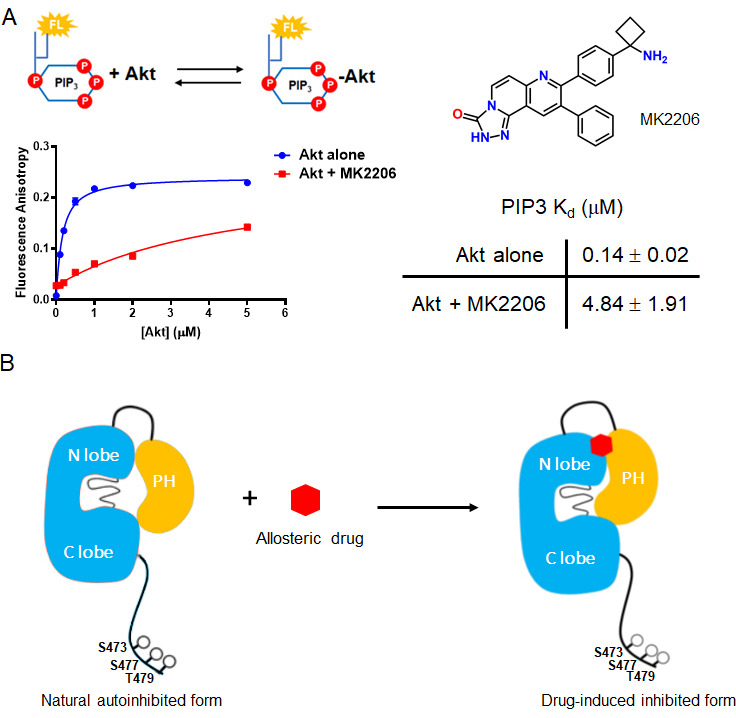
Figure 7—figure supplement 1. Allosteric inhibitors glue PH and kinase domains together and compete with PIP3.