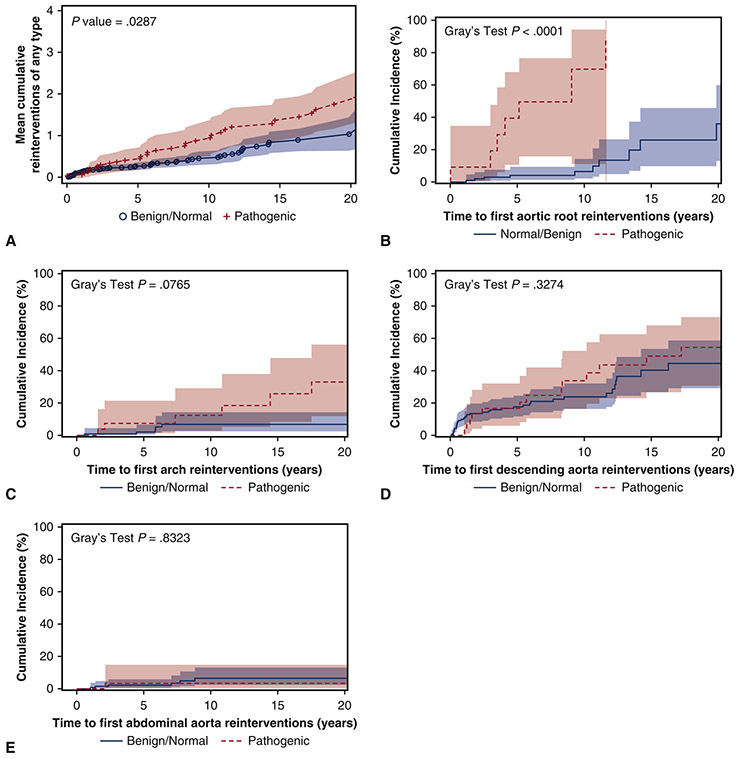
Figure 1.
A) The mean cumulative reinterventions per patient after thoracic aortic dissection was significantly higher in the pathogenic group than the benign/normal group. All aortic reinterventions were used to calculate the mean cumulative incidence. The cumulative incidence (CI) of first aortic root reintervention (B) was significantly higher in the pathogenic group (9-year CI: 70% vs. 6%). However, the cumulative incidence of first aortic arch reintervention (C), first descending thoracic aorta reintervention (D), and first abdominal aortic reintervention (E) were not significantly different between groups. Death was used as a competing factor.