Figure 5.
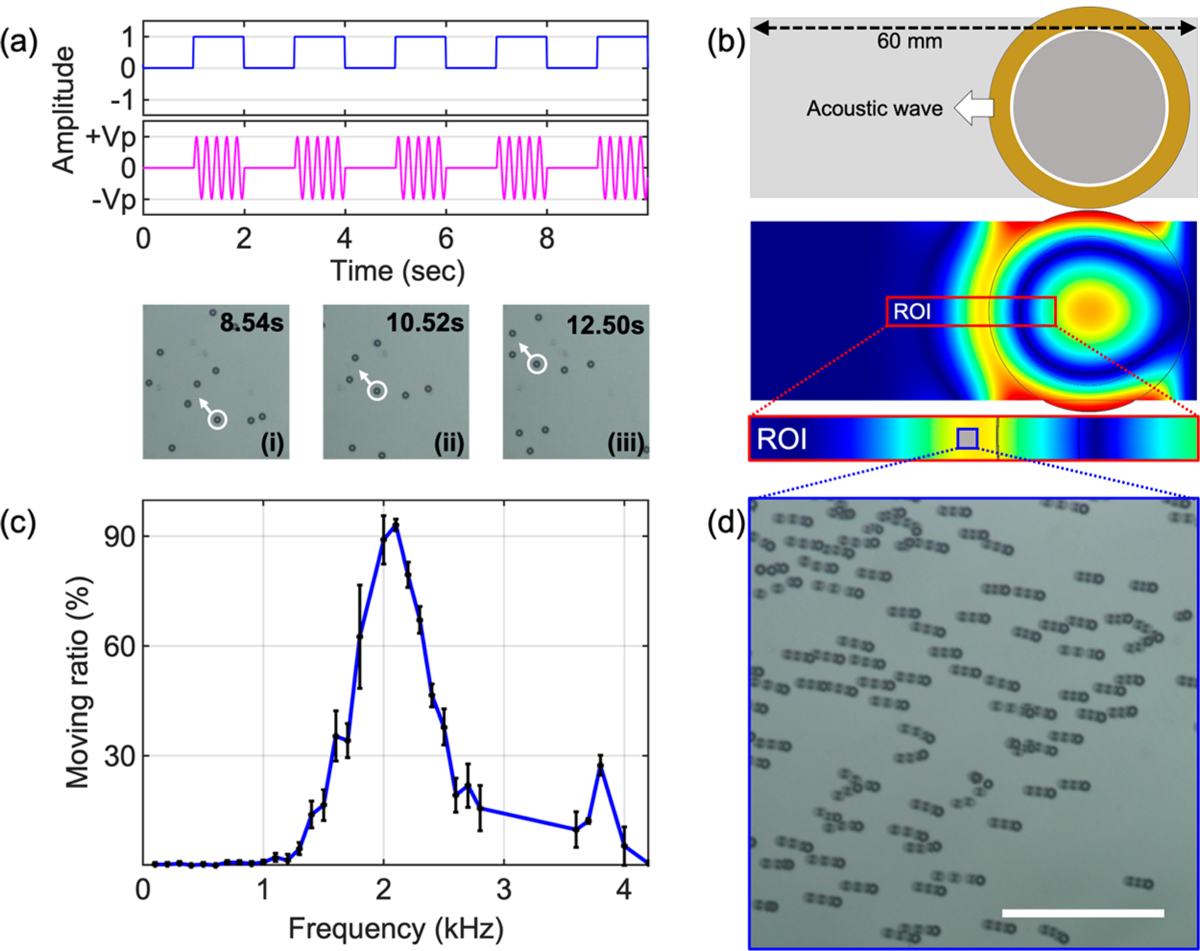
Acoustofluidic particle manipulation. (a, top) Illustration of the burst mode excitation with a duty cycle of 50% and a burst period of 2 s. (a, bottom) Time-lapse images acquired every 2 s after the completion of each burst. (b, top) Schematic figure of the acoustofluidic device composed of a circular piezoelectric transducer bonded onto a glass coverslip. (b, bottom) COMSOL simulation result of the acoustic field in the coverslip. Waves propagate out from the transducer, pushing particles in the fluid domain. (c) Relationship between moving particle ratio and excitation frequency under a 3 VPP amplitude excitation. (d) Stacked image of PS-20 particle movement. The imaging area corresponds to the blue box area in (b). The scale bar is 300 μm.
