Extended Data Fig. 8. Transfer of young eosinophils is associated with alterations in muscle stem cell frequencies but not function.
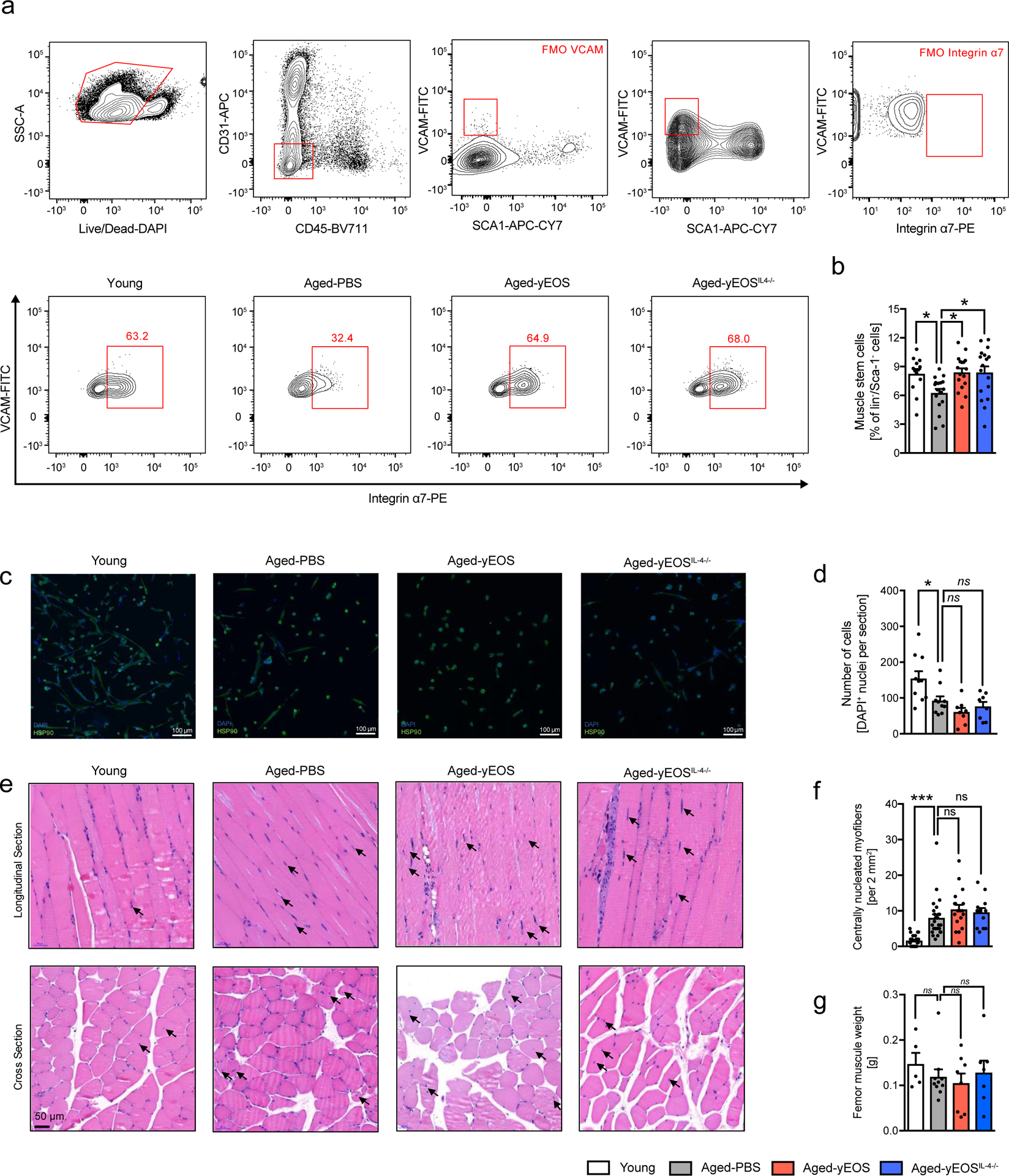
(a) Gating strategy and representative flow plots of CD31–, CD45–, Sca-1–, Vcam+ and integrin α7+ satellite cells in muscle of Young (n=13), Aged-PBS (n=17), Aged-yEOS, (n=17) and Aged-yEOSIL−4−/− (n=17) mice. (b) Quantification of muscle stem cell frequencies in indicated groups (c) Representative photographs of immunofluorescent stained sort-purified and differentiated satellite cells. (d) Quantification of cell colony formation of sort-purified muscle stem cells of Young (n=10), Aged-PBS (n=10), Aged-yEOS (n=8) and Aged-yEOSIL−4−/− (n=8) mice (e) Representative H&E stained longitudinal and cross-sectional quadriceps femoris in indicated groups. (f) Quantification of centrally nucleated myofibers in sections of Young (n=26), Aged-PBS (n=26), Aged-yEOS (n=18) and Aged-yEOSIL−4−/− (n=13) mice. (g) Muscle weight (femur) was measured in Young (n=5), Aged-PBS (n=9), Aged-yEOS (n=8) and Aged-yEOSIL−4−/− (n=7) mice. Data (a-f) are pooled from 2 independently performed experiments except for g (one experiment has been performed). Statistical significance was calculated by one-way ANOVA followed by two-tailed post-hoc Dunnett’s multiple comparison test against the aged-PBS treated group. Data are shown as individual data points with mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
