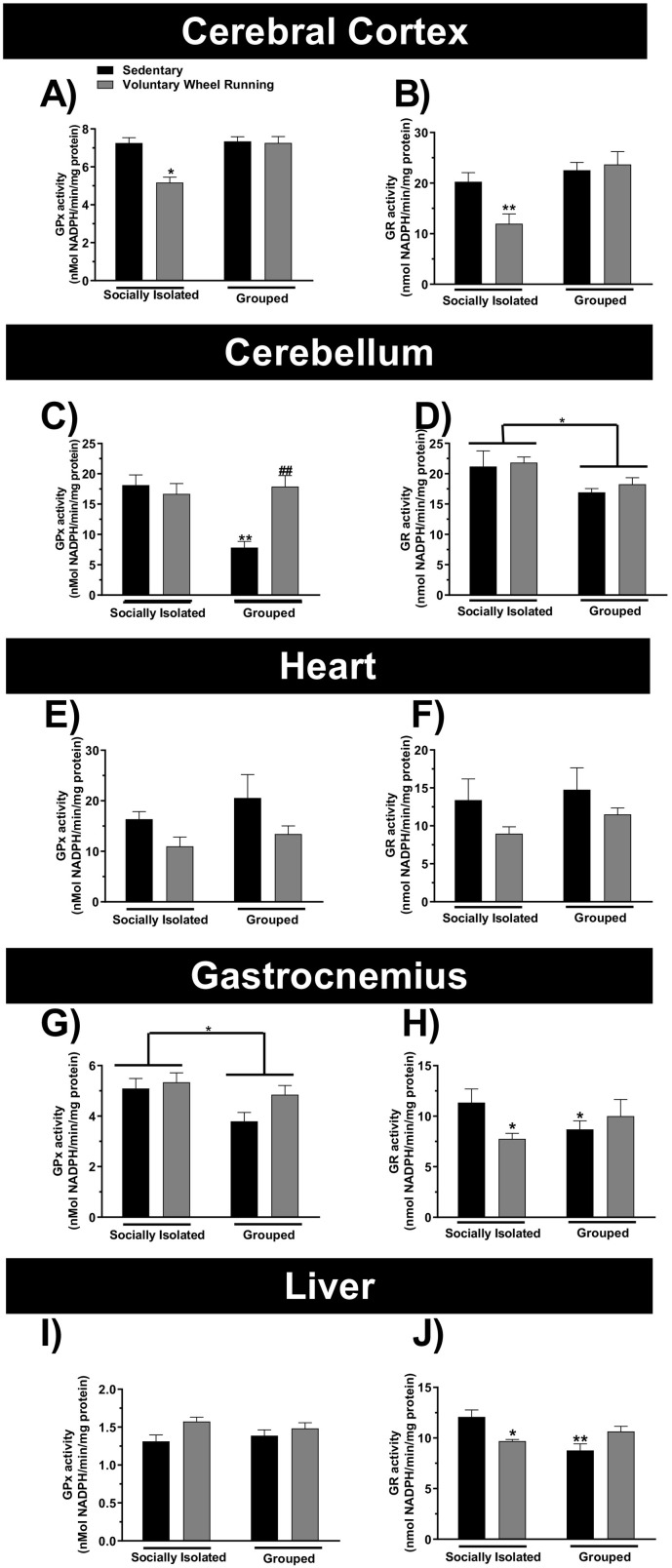
Fig. 4.
Physical activity and/or chronic social isolation induce alterations on the glutathione peroxidase (GPx) or glutathione reductase (GR) activities. The effect of physical activity on the GPx or GR activities in the cerebral cortex (Panels A and B, respectively), cerebellum (Panels C and D, respectively), heart (Panels E and F, respectively), gastrocnemius (Panels G and H, respectively), liver (Panels I and J, respectively) of the socially isolated or grouped mice. ⁎p < 0.05, ⁎⁎p < 0.01 as compared to sedentary socially isolated mice. #p < 0.05 as compared to sedentary grouped mice (n = 6; two-way ANOVA followed by Newman-Keuls post-hoc test).