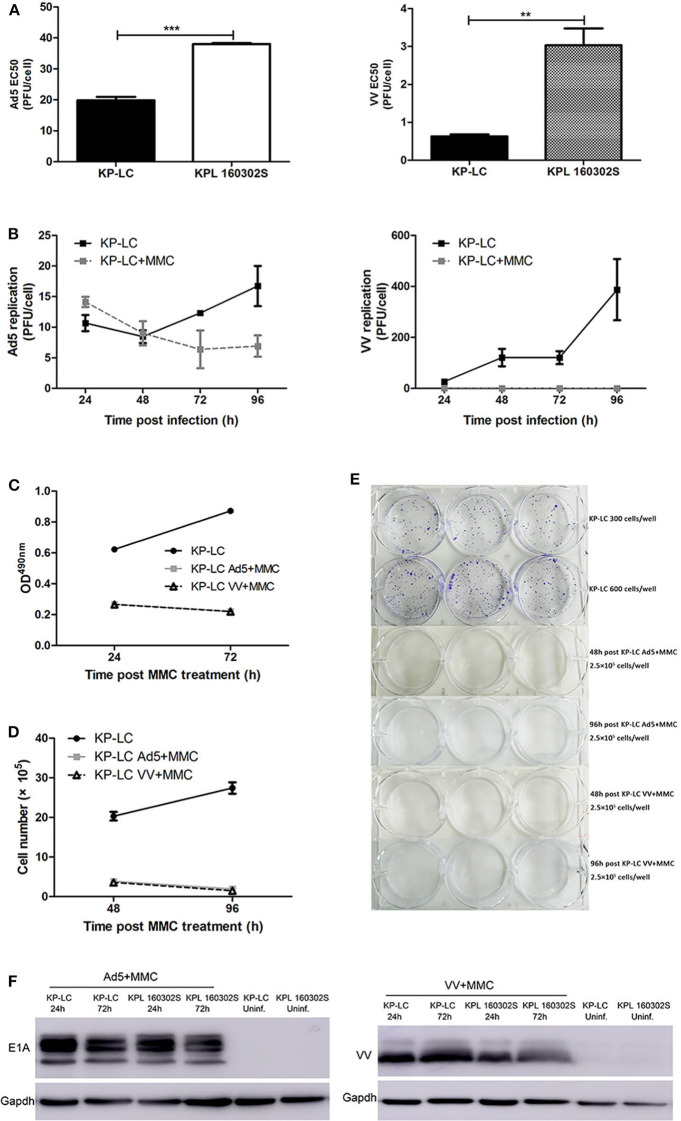
Figure 2.
AdV and VV can infect and replicate in transformed iPSCs and mitomycin-C treatment inhibits ongoing replication and tumor cell proliferation. (A) Cytotoxicity of Ad5 or VV on iPSC-derived KP-LC cells and KPL 160302S lung tumor cells. Cell death was determined by MTS assay 144 h post-infection. Mean EC50 values ± SEM are shown. (B) Production of infectious Ad5 or VV virions in KP-LC cells. Cells were infected with virus and were untreated or treated with mitomycin C. Mean viral replication ± SEM was determined at 24 h intervals for 96 h by TCID50 assay. JH293 cells for Ad5 or CV1 cells for VVL15-RFP. (C) Cell proliferation of KP-LC cells after infection and mitomycin-C treatment was determined using MTS assay at 24 and 72 h post-mitomycin C treatment. Mean OD490nm values ± SEM are shown. n = 3/group. (D) Cell proliferation of KP-LC cells after infection and mitomycin-C treatment was determined by cell counting at 48 and 96 h post-mitomycin C treatment. n = 3/group. (E) Plate colony formation of KP-LC cells after infection and mitomycin-C treatment. (F) Viral protein expression was determined in KP-LC or KPL 160302S cells at 24 and 72 h post-infection +/– mitomycin C treatment of cells. Anti-E1A was used to confirm AdV protein expression. Anti-VV coat protein was used to confirm VV protein expression. GAPDH was used as a loading control. **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001.