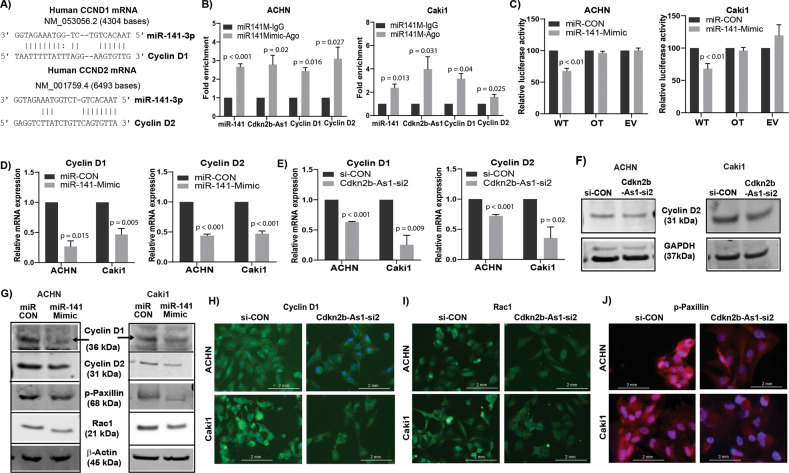
Fig. 6. miR-141/CDKN2B-AS1 interaction negatively regulates Cyclin-D and its downstream effectors in RCC.
a Predicted binding sites of miR-141 in cyclin-D1 and cyclin-D2 sequences. b RIP assay using Ago2 and IgG antibody (control) showing fold enrichment of miR-141, cyclin-D1, cyclin-D2, and CDKN2B-AS1 to Ago2 compared IgG controls in miR-141 overexpressing RCC cells. c Luciferase assays showing decreased reporter activity after co-transfection with either wild-type (WT), off-target (OT) cyclin-D2 or luciferase control constructs (EV) with miR-CON/miR-141 in ACHN and Caki1 cells. d, e Relative mRNA expression of cyclin-D1 and cyclin-D2 in both cell lines after miR-141 overexpression and CDKN2B-AS1 knockdown respectively. f Immunoblots showing changes in cyclin-D2 protein after CDKN2B-AS1 knockdown in ACHN and Caki1 cells. g Western blot analysis showing protein levels of cyclin-D1, cyclin-D2, pPaxillin, rac1, and β-actin (control) in ACHN and Caki1 cells overexpressing miR-141. h–j Immunostaining of cyclin-D1, rac1 (green) and pPaxillin (red) counterstained with DAPI (blue) in ACHN and Caki1 cells after transfecting with si-CON/CDKN2B-AS1-si2, scale bar: 2 mm (right bottom).