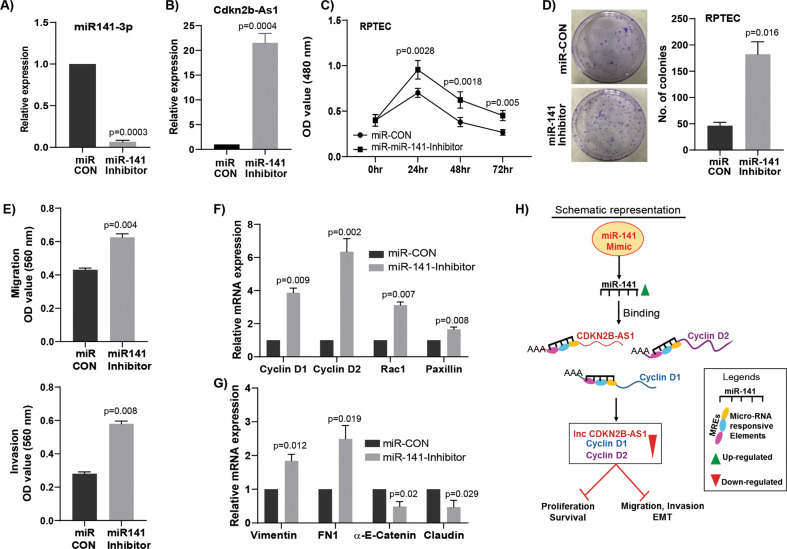
Fig. 7. Inhibition of miR-141 exerts tumorigenic attributes in nonmalignant RPTEC cells.
a Relative miR-141 expression after transient transfection of miR-141 inhibitor compared to miRNA inhibitor control (miR-CON) in non-malignant RPTEC cells. b Relative expression of CDKN2B-AS1 in miR-141 inhibited RPTEC cells. c miR-141 inhibition in RPTEC cells induced cell proliferation. d Increased colony formation in miR-141 inhibited RPTEC cells as compared to control. e An increase in migration and invasion of miR-141 inhibited RPTEC cells. f, g A significant increase in the mRNA expression of cyclin-D1, cyclin-D2, rac1, paxillin, vimentin, fibronectin (FN1) along with decrease in the expression of α-E-catenin and claudin in RPTEC cells with inhibition of miR-141 compared to control. h Schematic representation showing knockdown of CDKN2B-AS1 due to overexpression of miR-141 results in decreased cyclin-D1 and cyclin-D2 expression which in turn inhibits proliferation/survival/invasion and migration pathways.