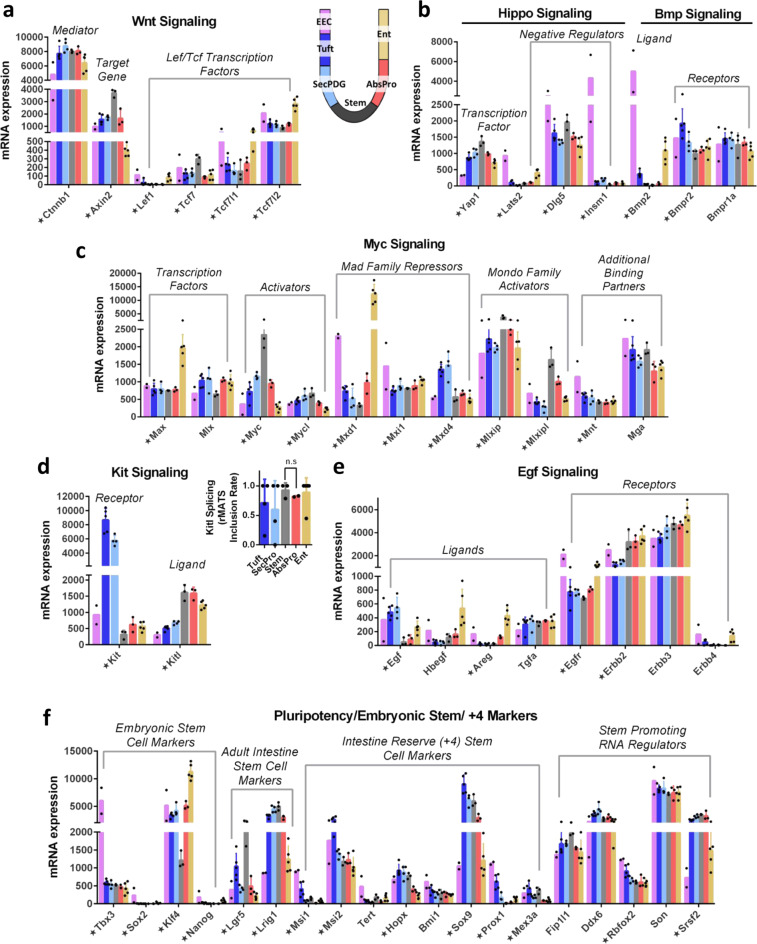
Fig. 7. Fate commitment and signaling characteristics of mature crypt cells.
a mRNA expression of key Wnt signaling factors including Lef/Tcf transcription factors, β-catenin mediator (Supplementary Fig. 27a), and downstream target gene Axin2. b mRNA expression of Hippo and Bmp signaling components. c mRNA expression of Myc signaling components including strong expression of repressive transcription factors. d mRNA expression of Kit signaling components including ligand (high in stem and absorptive), receptor (high in SecPDG and tuft). Splicing rates of Kitl in crypt cell types showed predominance of exon 6 inclusion, which encodes a protease cleavage site for release and secretion of Kit ligand (inset). e mRNA expression of Egf signaling components including select epithelial ligand expression and receptors expressed in all cells. Egfr is elevated in EEC (Supplementary Fig. 28), whereas the lowest levels of Erbb2 is in SecPDG and tuft. f mRNA expression of stem promoting markers including classic adult intestine stem cell markers, embryonic stem cell markers, intestinal reserve (+4) stem cell markers, and RNA regulators showing enriched expression in some differentiated cell types. Star annotation by gene name symbolizes significant differential mRNA expression in at least one cell type compared to stem (padj < 0.01). mRNA expression values are normalized counts and error bars are standard deviation. mRNA differential expression analysis was performed with the following biological replicate numbers: stem = 3, AbsPro = 3, SecPDG = 4, tuft = 5, Ent = 5, and EEC = 2.