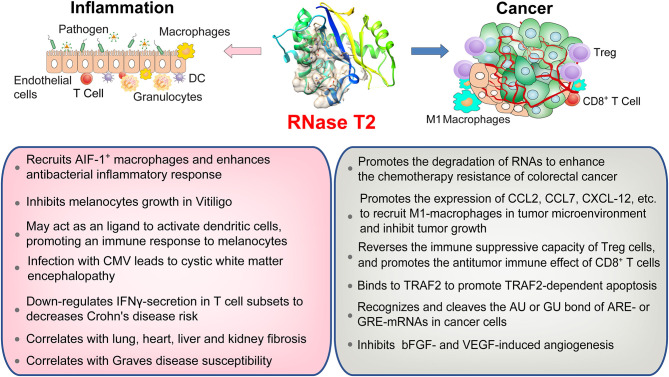
Figure 2.
An overview of RNase T2 functions in inflammation and cancer. RNase T2 is critical for defending against the infection of exogenous pathogens. RNase T2 is secreted by granulocytes to recruit macrophages and trigger the innate immune response during pathogen infection. RNase T2 has antitumorigenic activity through promoting cancer cell apoptosis, inhibiting angiogenesis, and enhancing antitumor immunity.