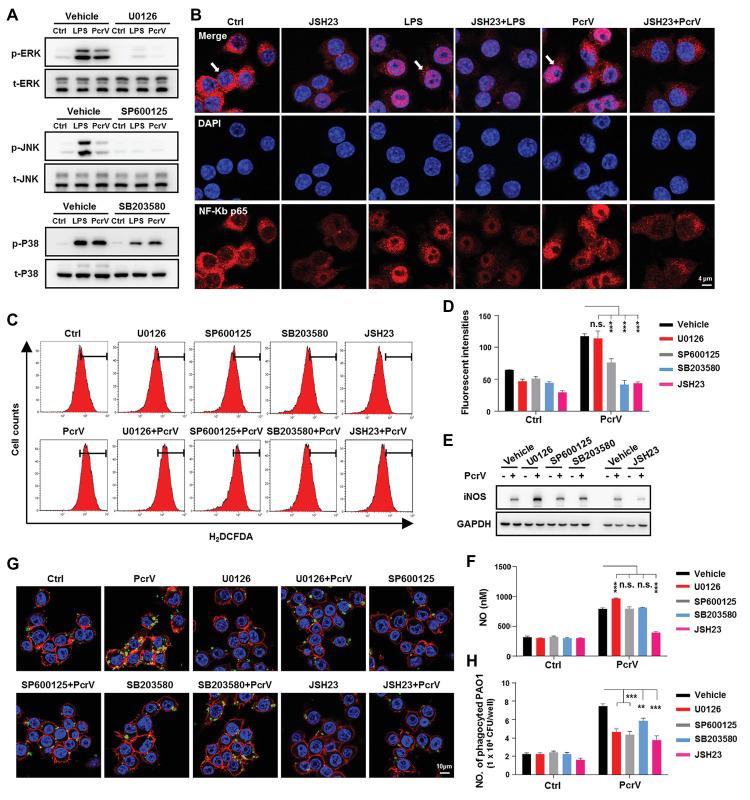
Figure 6.
Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) and NF-κB signaling pathways are involved in PcrV-mediated activation of M1 macrophages and increasing of phagocytosis. Raw264.7 cells pretreated with the corresponding inhibitors U0126 (5 μM), SP600125 (10 μM), SB203580 (5 μM), and JSH23 (15 μM) for extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), p38 MAPKs, and NF-κB, respectively, were primed by LPS + IFNγ (named as LPS group) or PcrV (10 μg/ml) for 6 h. The total and phosphorylation levels of JNK, ERK, and p38 MAPKs were analyzed by western blot (A). The cellular translocation of NF-κB was visualized by immunofluorescence staining (B). NF-κB was labeled with AF647-conjugated anti-NF-κB p65 antibody (red); cellular nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). ROS (C,D) and iNOS (E) production were analyzed by flow cytometry and western blot, respectively. (F) The concentration of NO in the culture supernatant of Raw264.7 treated with the indicated compound for 24 h was detected by NO detection kit. Raw264.7 pretreated with the corresponding inhibitors was primed by PcrV (10 μg/ml) for 6 h. The cells were then co-cultured with static PAO1 biofilms (MOI = 10) for 30 min. Phagocytosis was detected by immunofluorescence staining (G) and CFU enumeration (H). Cytoskeleton was labeled with phalloidin (red); PAO1 was visualized by FITC anti-PAO1 antibody (green); cellular nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Unpaired Student’s t test was used for statistical analysis (D,F,H). **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; n.s. indicates no significance.